2.4—Roller Bearings
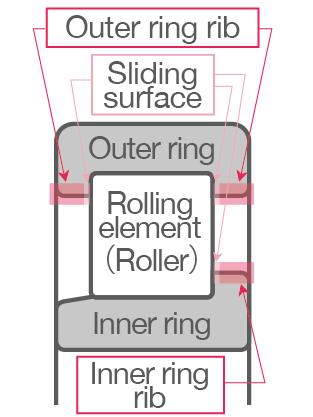
Roller bearings use rollers as the rolling elements. Rollers in the bearings make linear contact with the outer and inner rings, allowing for higher load capacity than ball bearings, which make point contact. However, roller bearings are not well-suited for high-speed rotation.
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
- The rollers in cylindrical roller bearings (CRBs) make linear contact with the raceway.
- Because CRBs have a contact angle of zero, they have high radial load capacity and are used with primarily radial loads.
- Low sliding friction between the rolling elements and the ring rib allows cylindrical roller bearings to support the highest speeds among roller bearings.
- All types have separable rings for easy mounting and dismounting.
- The roller and outer ring assembly and the inner rings of interchangeable CRBs can be combined with other rings with no loss in function, while non-interchangeable CRBs must be used as shipped. Interchangeable types make it easy to manage parts during assembly and inspections.
- CRBs without ribs on the inner or outer rings can handle shaft elongation and contraction.

Cylindrical Roller Bearings: Types and Characteristics
- Types NU, N, NNU, and NN are suitable as free-end bearings.
- Types NJ, and NF can sustain limited axial loads in one direction.
- Types NH, and NUP can be used as fixed-end bearings.

Single-row cylindrical roller bearings

Double-row cylindrical roller bearings
Design of cylindrical roller bearings

Types of single-row cylindrical roller bearings

Types of double-row cylindrical roller bearings
Double-row cylindrical roller bearings provide high rigidity under radial loads and are often used in the main spindles of machine tools.
Needle Roller Bearings
- Needle roller bearings feature rolling elements with a roller diameter (DW) of 6 mm or less and a roller length (LW) 3 to 10x their diameter.
The ratio of the outside diameter to the roller inscribed circle diameter is small, providing high capacity for radial loads.
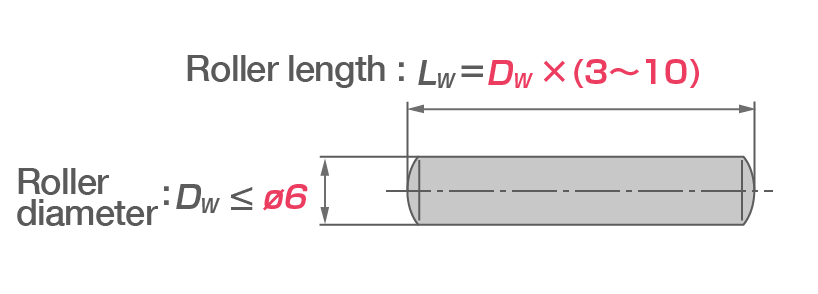
Needle roller criteria: DW > ⌀ 6 and LW = DW x (3 to 10)
- Needle roller bearings come in three types:
-Drawn cup needle roller bearings with outer rings made of a special steel alloy,
-Solid needle roller bearings with machined outer rings
-Cage & roller assembles and stud-type track rollers (cam followers) with no raceway rings. - Needle roller bearings are broadly defined by their shape and the presence or absence of inner rings and cages. ⇒ Ex: (R) NA48xx
- Cages are typically made of pressed steel.

Tapered Roller Bearings
- Tapered roller bearings (TRBs) feature trapezoidal tapered rollers guided by a large rib on the inner ring.
- As the bearings are usually are mounted in pairs, TRBs can support radial loads, axial loads, and moment loads.
- The appropriate internal clearance (or preload) can be set by adjusting the axial distance between the inner and outer rings.
- Double-row and four-row tapered roller bearings are also available.

The imagined conical apices formed by the roller surfaces and raceways converge at one point.
This creates pure rolling contact between the rollers and raceway with no sliding.
However, the rib receives the axial force generated on the rollers, creating sliding contact between the rib surface and roller end face. (α: Contact angle)

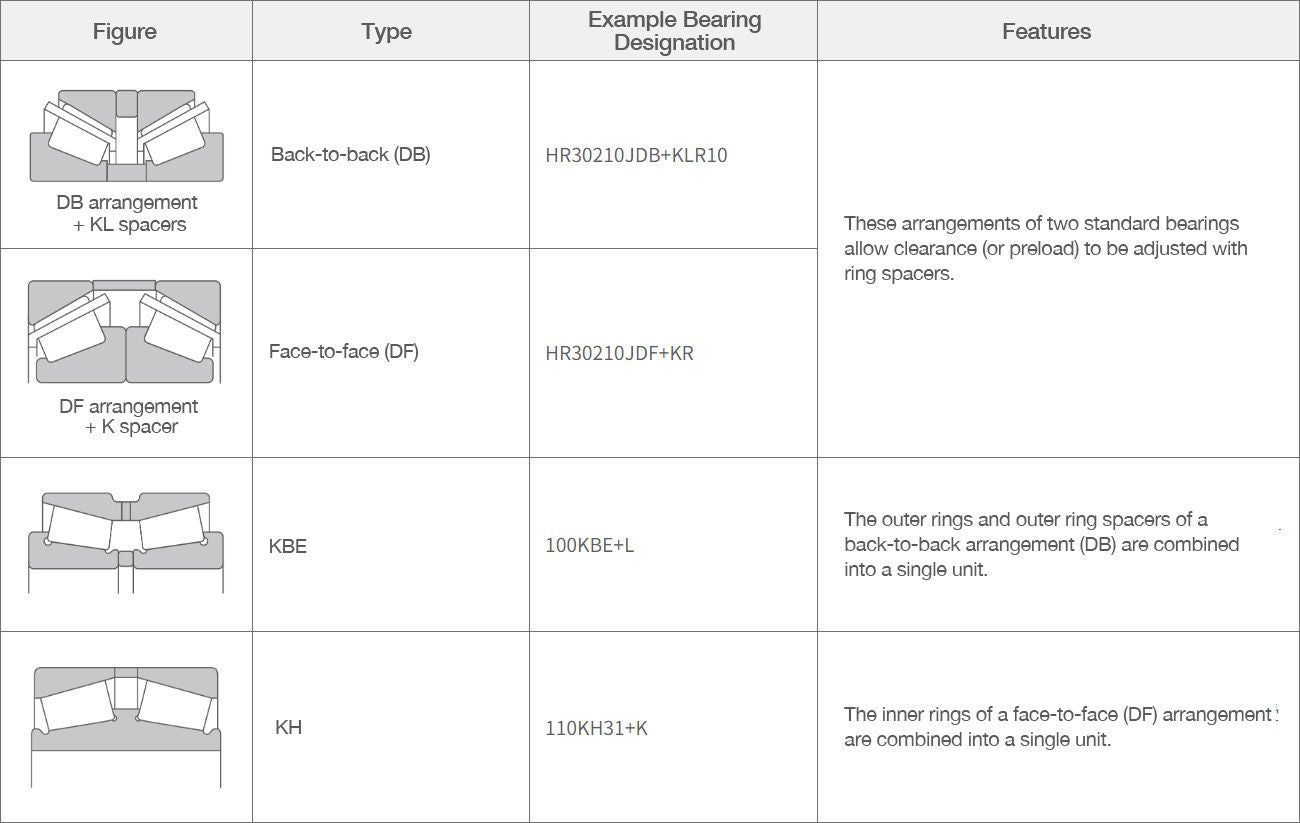
Characteristics of Tapered Roller Bearings and Arrangements
Spherical Roller Bearings
- Spherical roller bearings (SRBs) are self-aligning double-row bearings that feature an outer ring with a spherical raceway surface and barrel-shaped rollers.
- The central curvature of the outer ring raceway surface is aligned with the bearing center, making the bearing self-aligning.
- SRBs can support radial loads and axial loads in both directions.
- They have high radial load capacity suitable for applications with heavy or shock loads.
- SRBs automatically correct for deflection of the shaft/housing and off-centering so that no undue force is applied to the bearing.
- SRBs with tapered bore inner rings can be mounted directly on tapered shafts or on cylindrical shafts using an adapter (for easy installation) or withdrawal sleeve (for easy dismounting).

