2.5—Thrust Bearings
Thrust bearings use balls or rollers to support axial loads (loads in the direction of the rotating shaft).
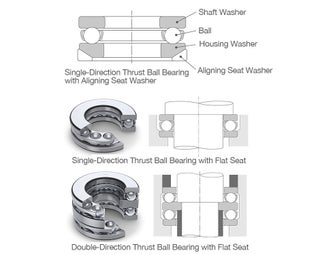
Thrust Ball Bearings
- The raceways of thrust ball bearings lie on housing washers and shaft washers, which serve the same function as the outer and inner ring in radial bearings.
- Double-direction types feature a central washer attached to the shaft.
- Single-direction types can support axial loads in one direction, while double- direction types support axial loads in both directions.
- Some models have an aligning seat attached to the housing washer to reduce the effect of mounting errors.
- Cages are typically made of pressed steel for small bearings, while large bearings use machined cages.
Spherical Roller Thrust Bearings
- The barrel-shaped rollers in spherical roller thrust bearings are arranged to create diagonal rolling surfaces. Since the housing raceway is spherical, the bearing is self-aligning.
- Spherical roller thrust bearings have very high capacity for axial (thrust) loads and can carry some radial load when an axial load is applied.
- Oil lubrication is recommended even at low speeds to maintain proper lubrication in areas such as the contact surfaces between the roller and shaft washer rib.
- The raceways of thrust roller bearings lie on housing washers and shaft washers, which serve the same function as the outer and inner ring in radial bearings.

