1.1—Differentiating Rolling Bearings
Rolling bearings are classified in several ways. In broad terms, bearing names reflect the load they support (radial or thrust/axial) and what kind of rolling elements are used (balls or rollers). They can be specified further by the shape of the rolling elements and how many rows are present, bearing size, whether the outer ring and inner ring are separated, and other characteristics.
Load Categories
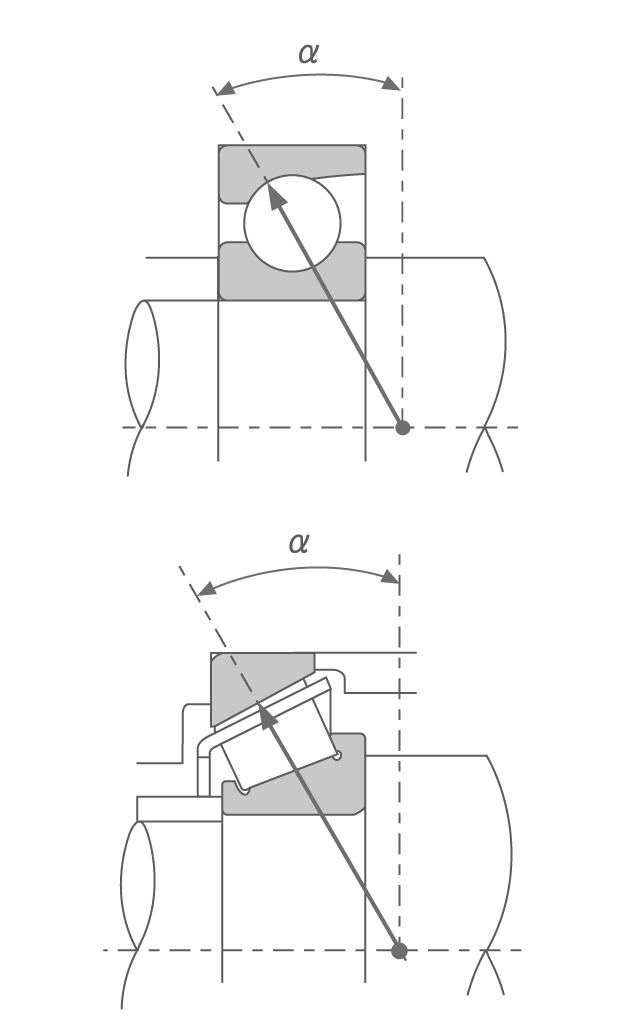
A bearing’s contact angle (α) refers to the angle between an imaginary line perpendicular to the bearing axis and another through the points where a rolling element contacts the inner and outer ring raceway surfaces under load.
The size of contact angle α determines whether a bearing is a radial or thrust type.
Contact Angle and Bearing Type
Radial bearings: 0° ≤ α ≤ 45° (primarily radial loads supported)
Thrust bearings: 45° < α ≤ 90° (primarily axial loads supported)
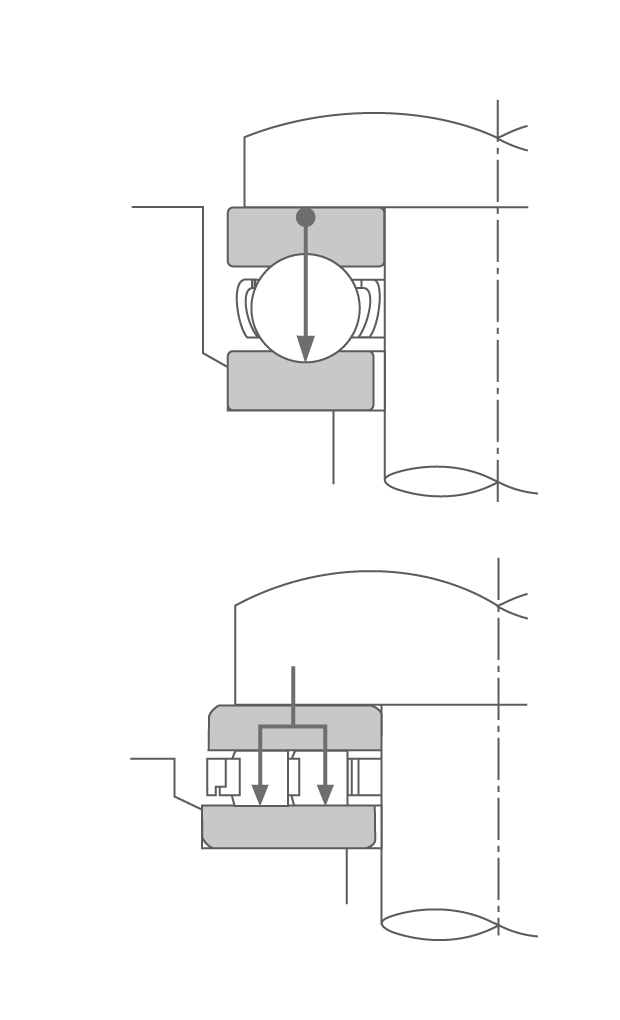
α = 0°
(Examples of radial bearings)

Contact angle α
(Measurement, examples of radial bearings)
α = 90°
(Examples of thrust bearings)
Rolling Element Categories
Ball Bearings
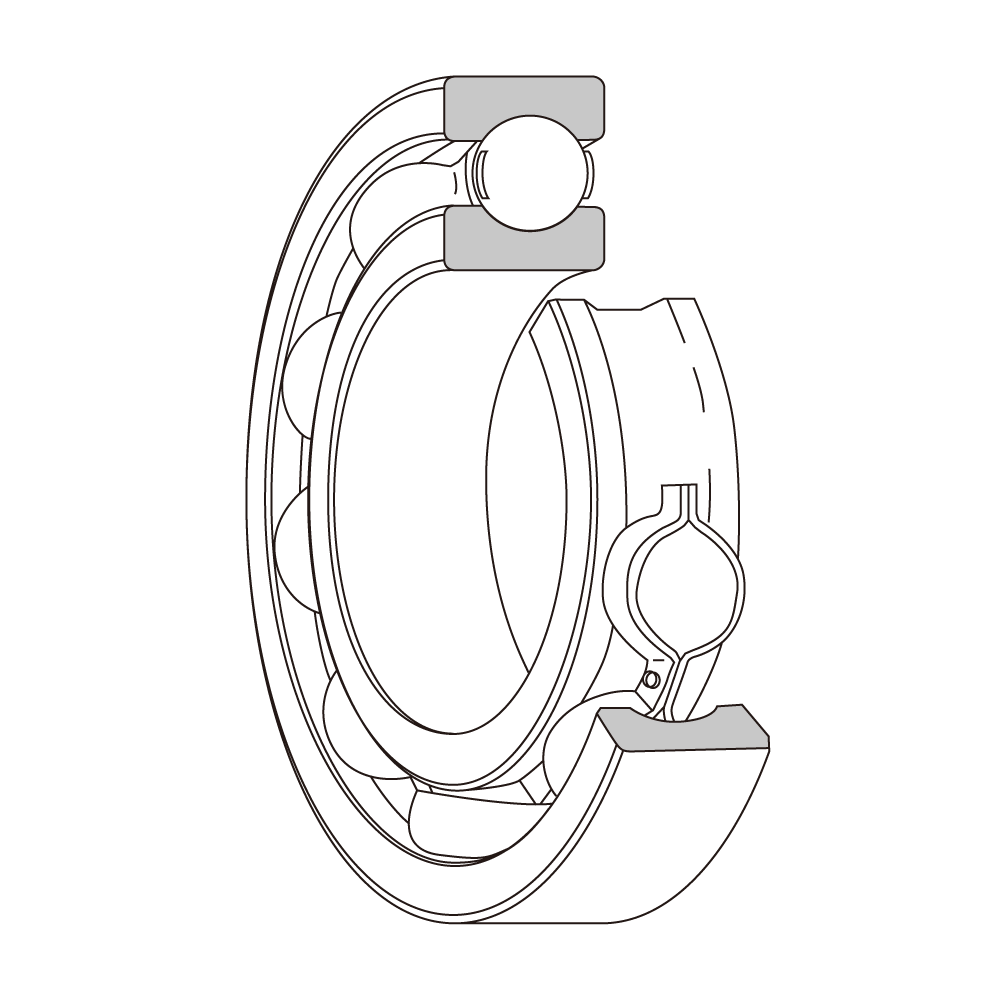
Deep groove ball bearing
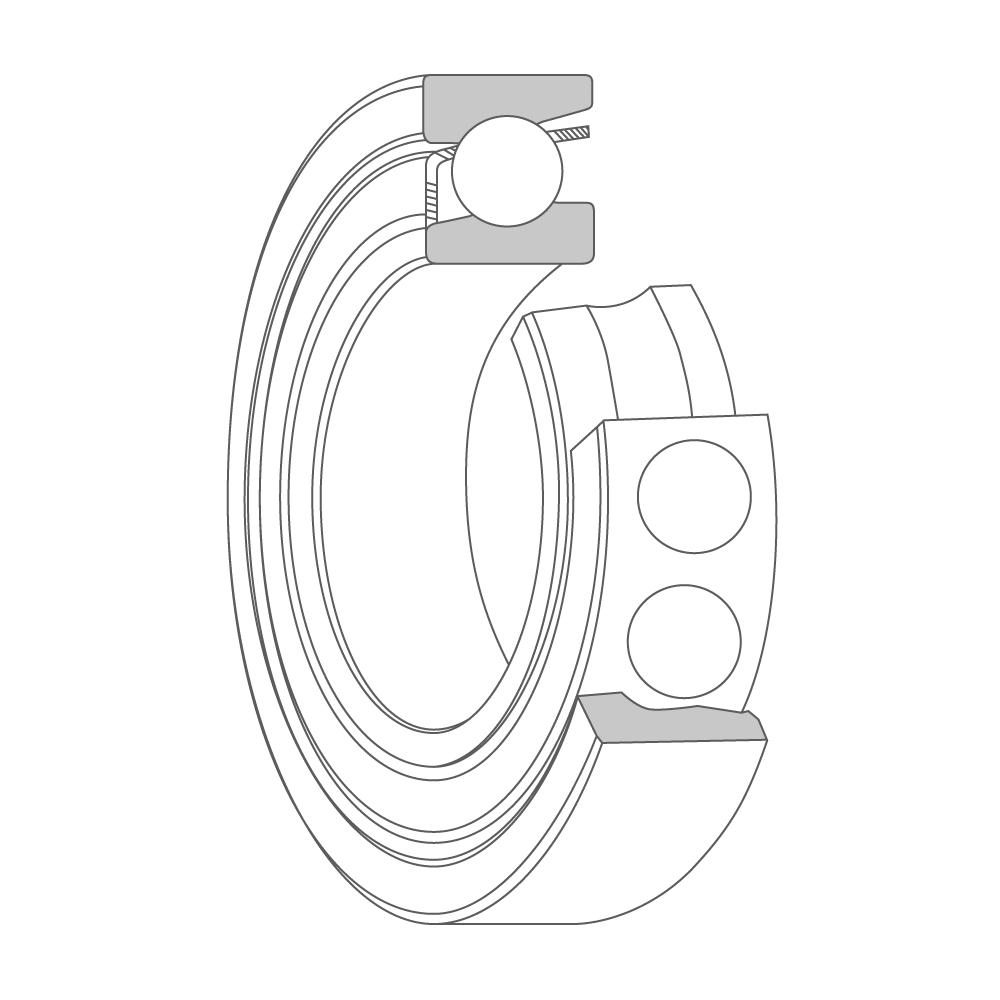
Angular contact ball bearing
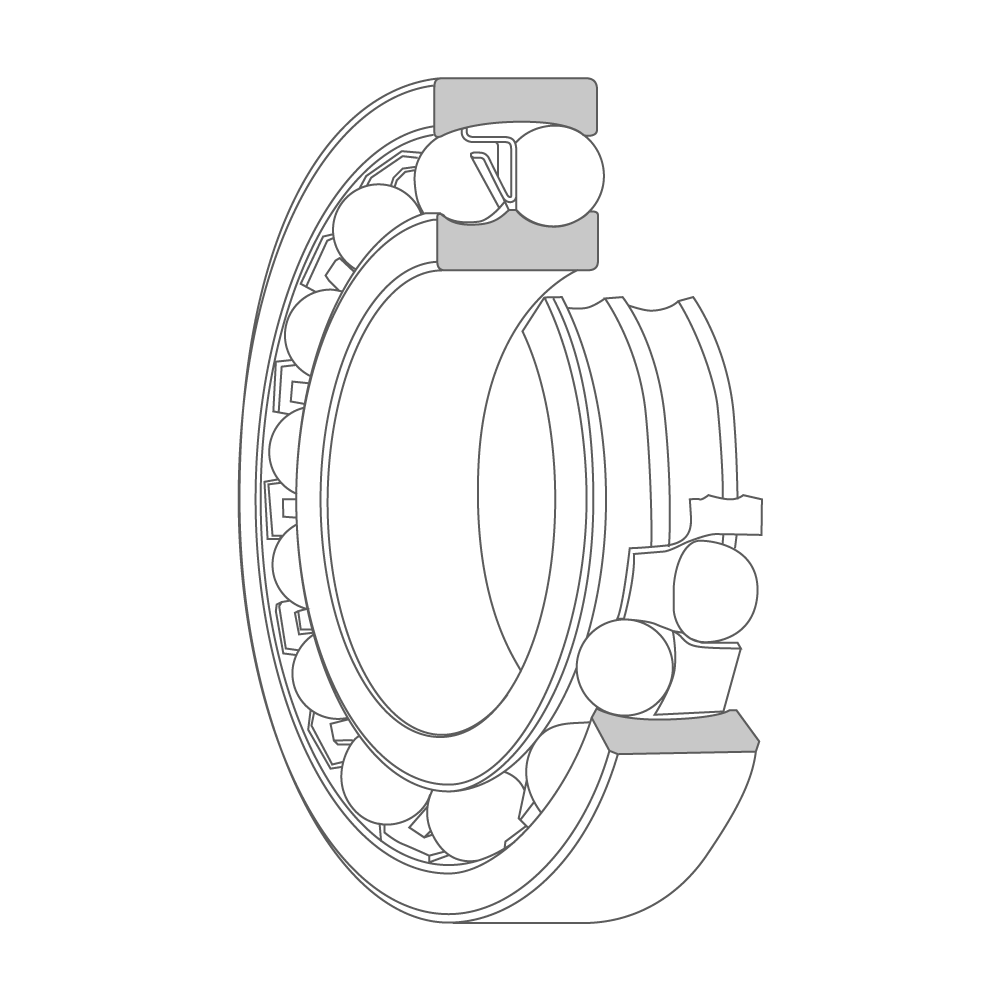
Self-aligning ball bearing
Roller Bearings

Tapered roller bearing
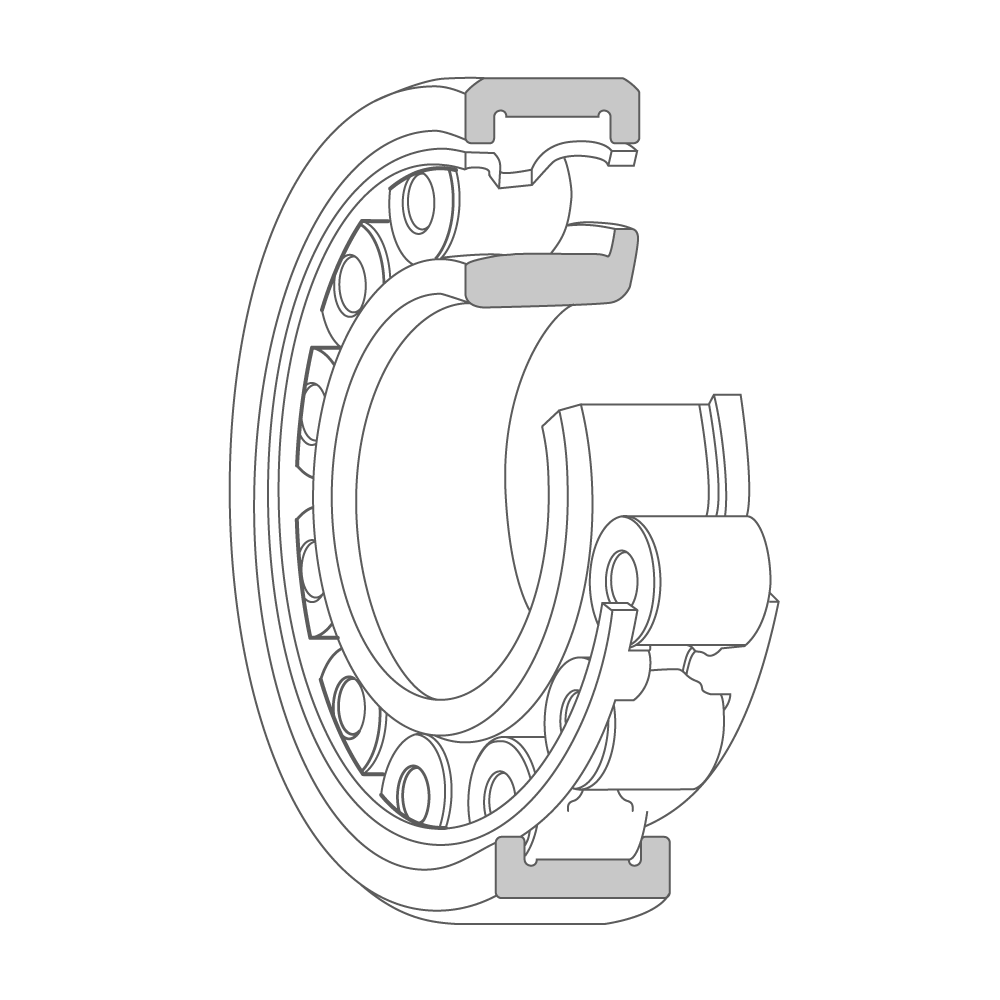
Cylindrical roller bearing
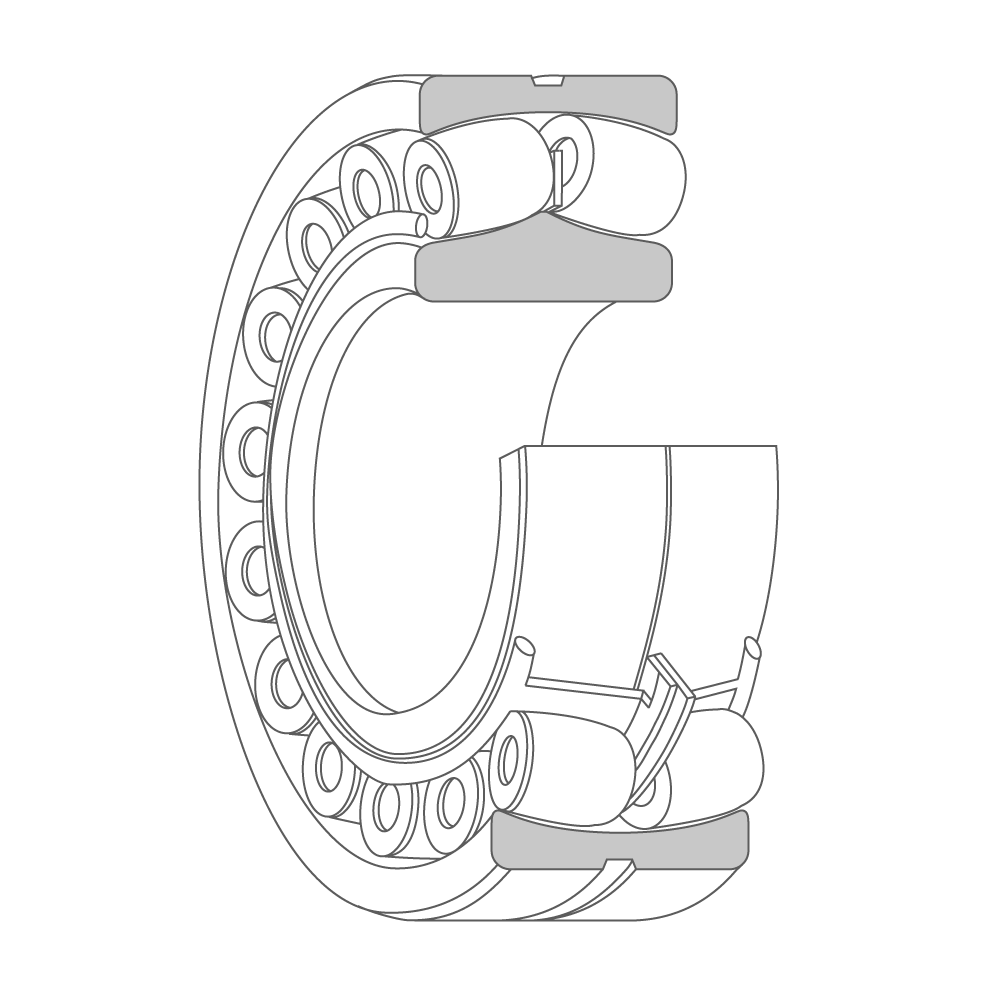
Spherical roller bearing
Number of Rows
Radial bearings are identified by the number of rows they have, with single-row, double-row, and multi-row varieties available.
Thrust bearings are additionally defined by the direction of loads they support, with single-direction or double-direction (multi-stage/tandem) variants available.
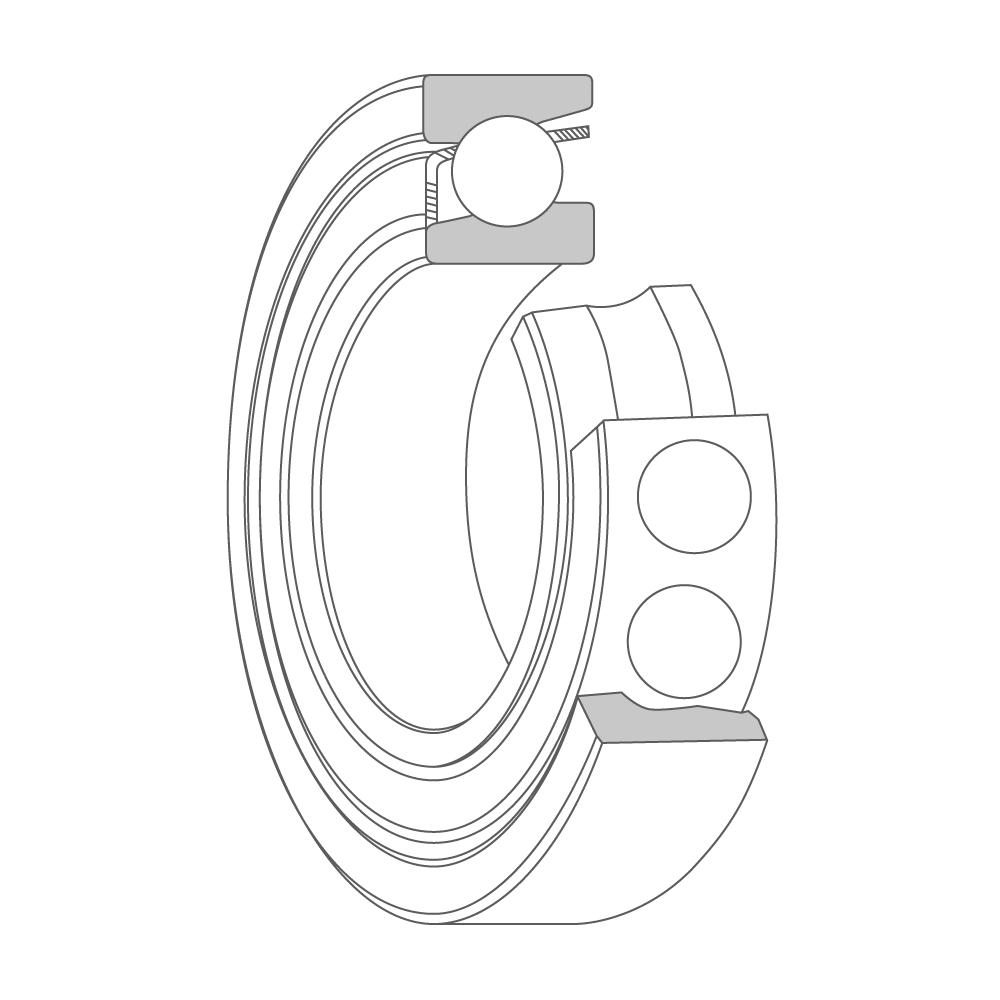
Single-row angular contact ball bearing
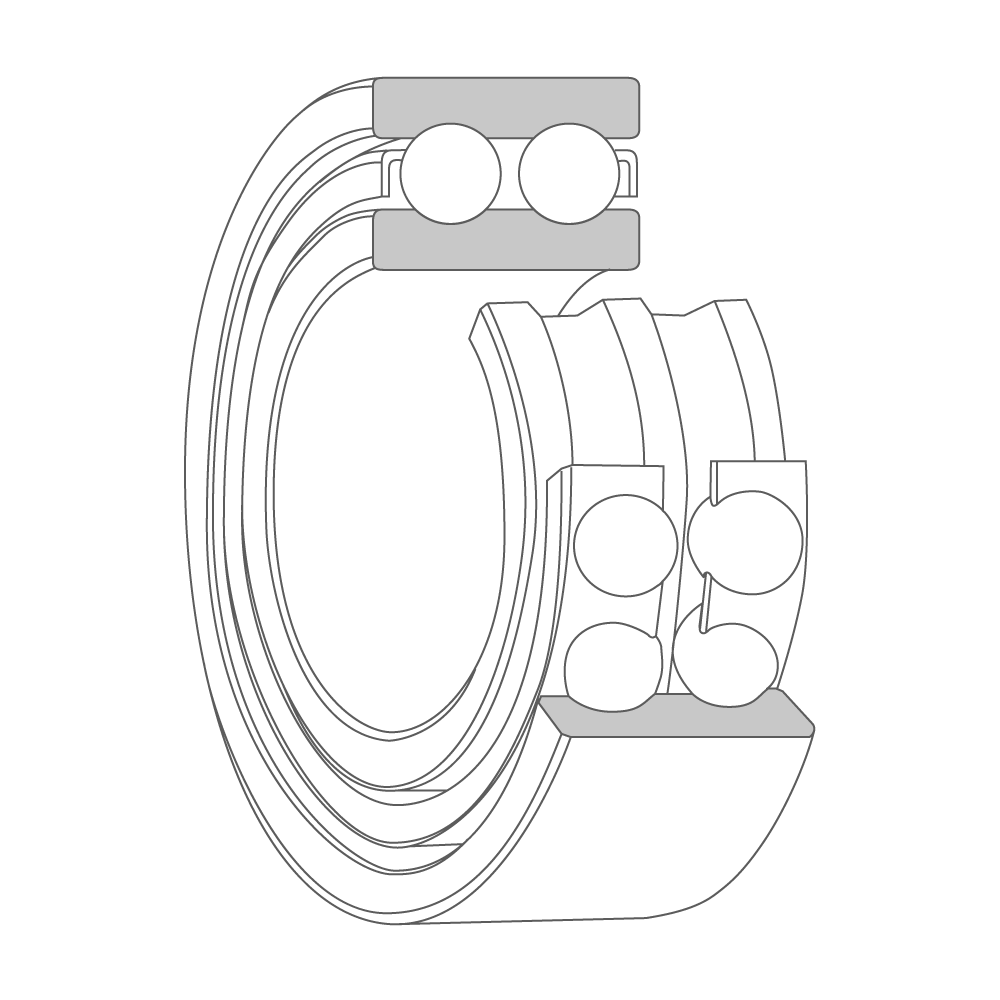
Double-row angular contact ball bearing
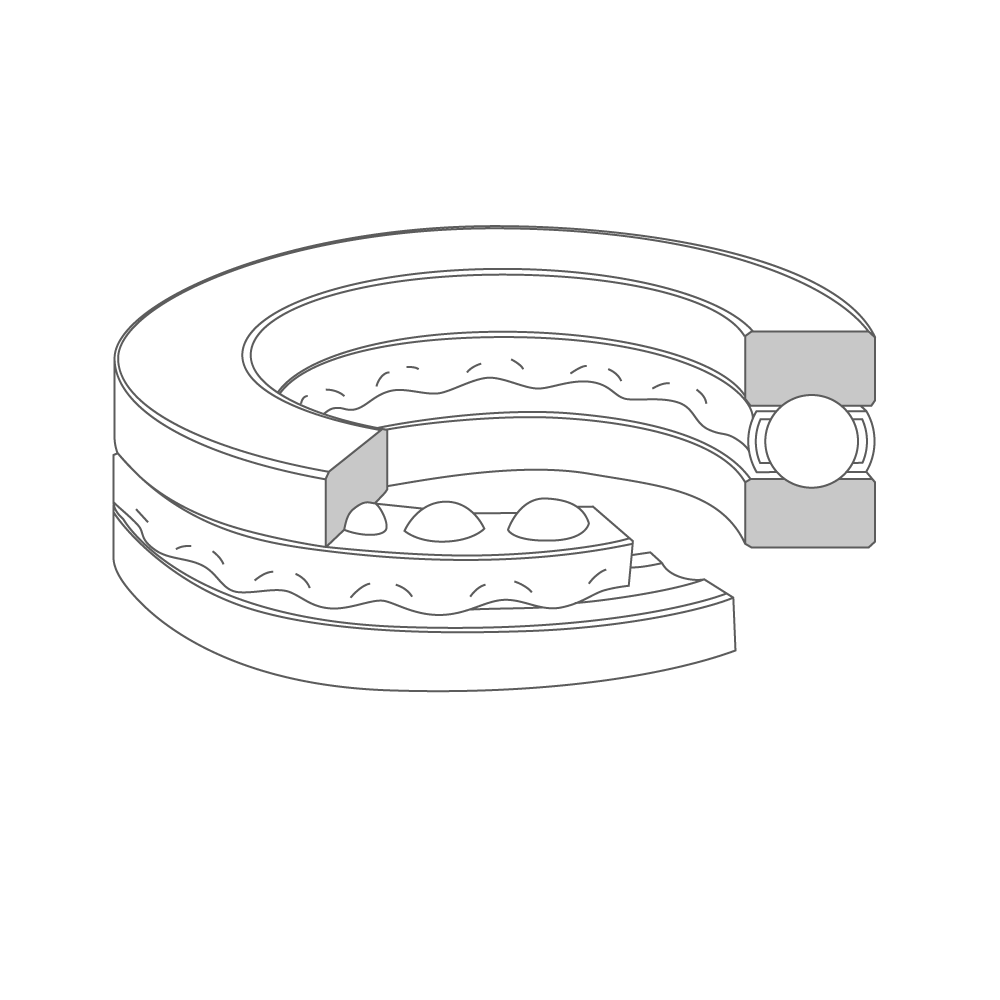
Single-direction thrust ball bearing
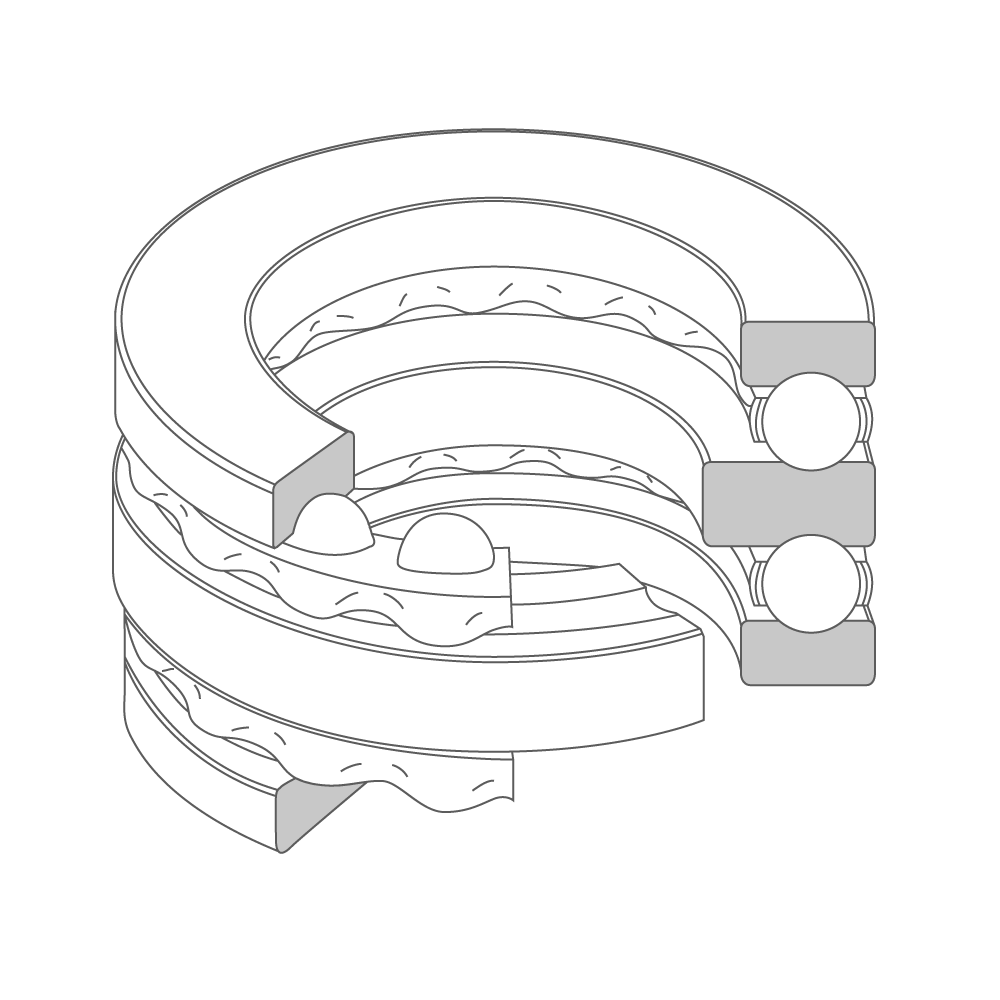
Double-direction thrust ball bearing
Ring Structure
The inner and outer rings of some bearings are separable, while others are inseparable.
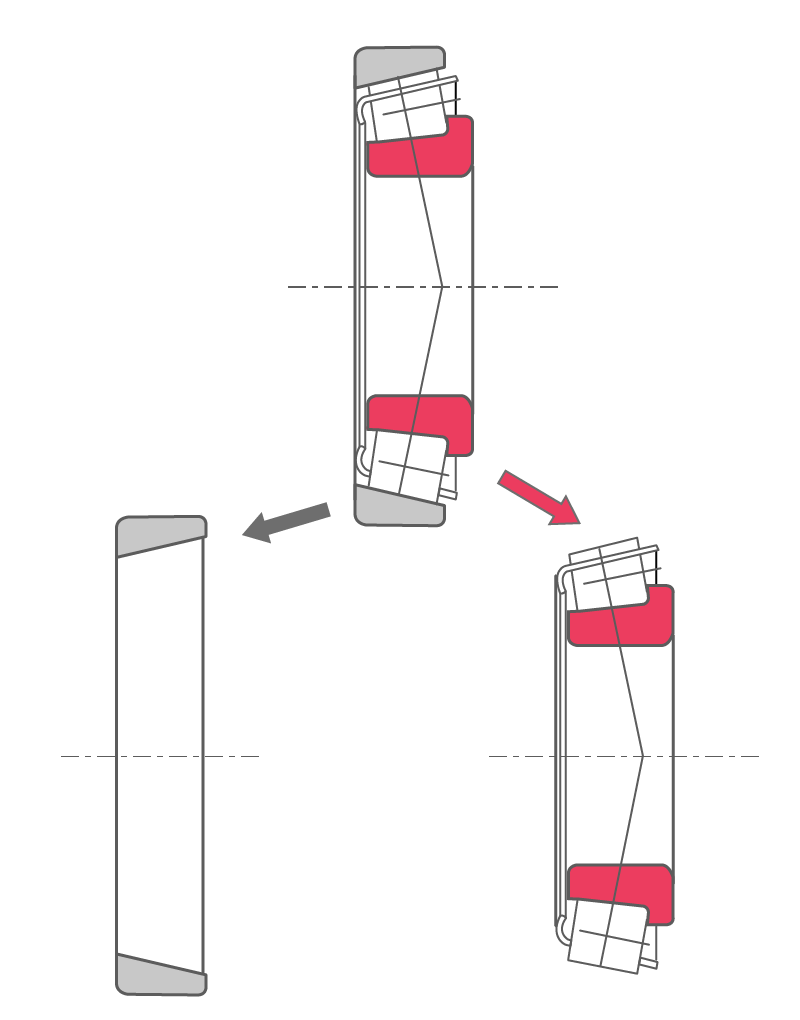
Separable tapered roller bearing
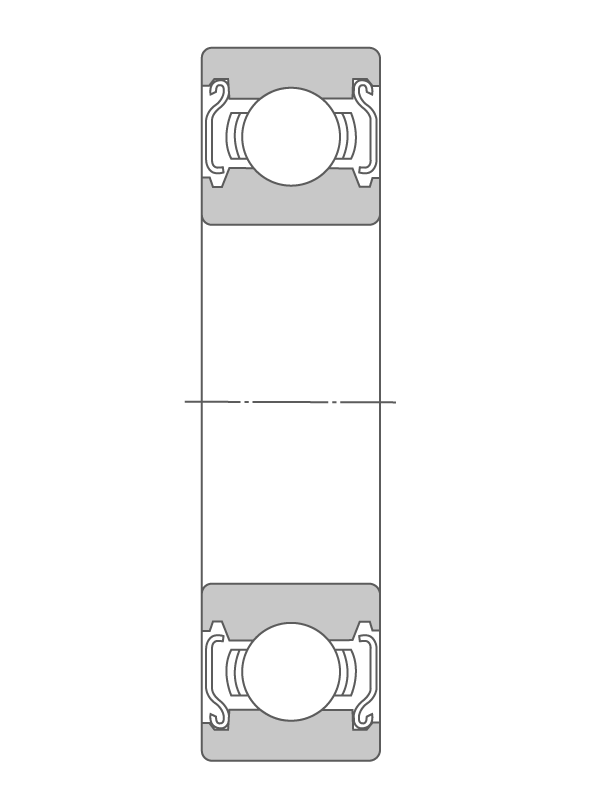
Inseparable deep groove ball bearing
Bearing Size
NSK bearing sizes differ slightly from those used in Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS).
| Size | Dimensions (d: Bore Diameter, D: Outside Diameter) (mm) |
|---|---|
| Miniature | D < Φ9 |
| Extra small | d < Φ10, D ≥ Φ9 |
| Small | d ≥ Φ10, D < Φ200 |
| Large | Φ200 ≤ D < Φ400 |
| Extra large | Φ400 ≤ D < Φ600 |
| Ultra large | Φ600 ≤ D |
