2.1—Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Ball bearings are said to account for about 70% of all the bearings used in the world. Deep groove ball bearings are the most common type of bearing, with a variety of seals and shield configurations available to extend bearing life.
Features of Deep Groove Ball Bearings
- As the most common bearing, deep groove ball bearings are found in a wide range of applications.
- Cages are typically made of pressed steel or resin.
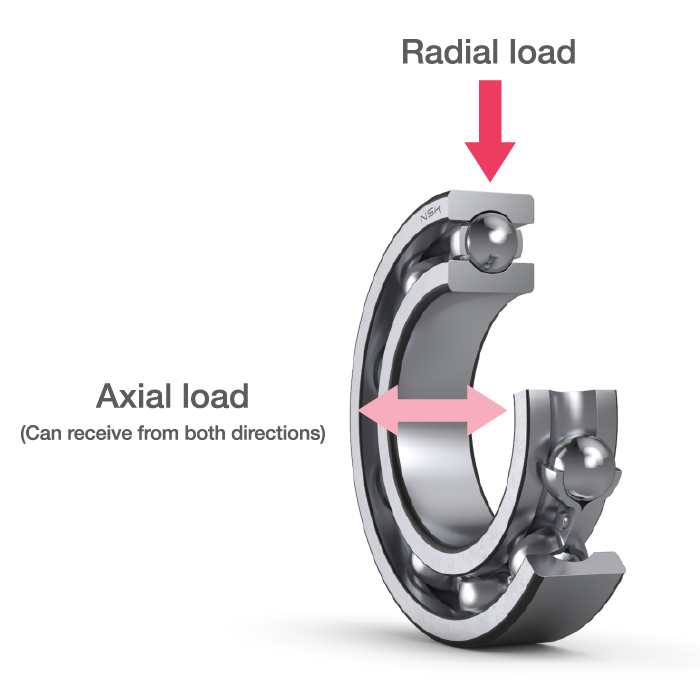
- They can handle both radial and axial loads.
- Unlike the linear contact found in roller bearings, ball bearings utilize point contact which allows them to support high speeds with low torque and low noise/vibration.
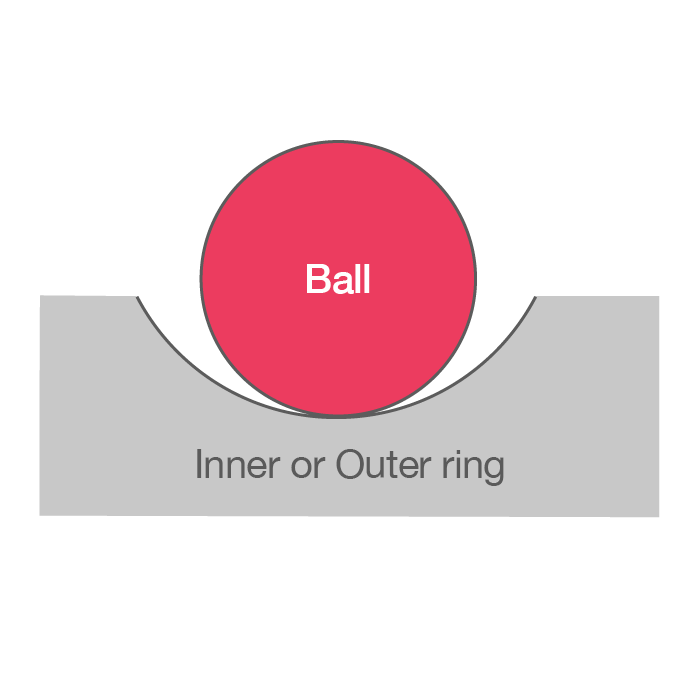
- The raceway groove in the inner and outer rings has a circular arc with a slightly larger radius than that of the balls.
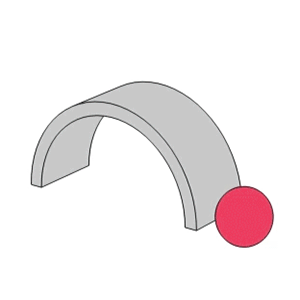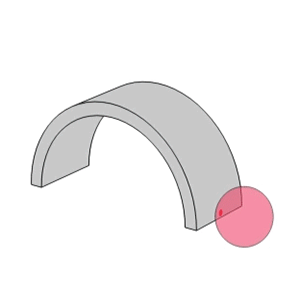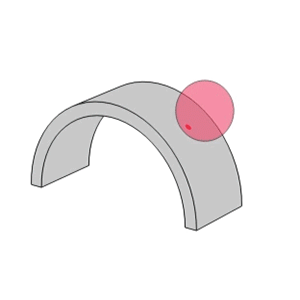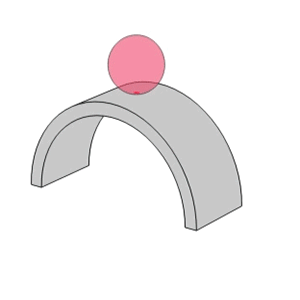
Point Contact
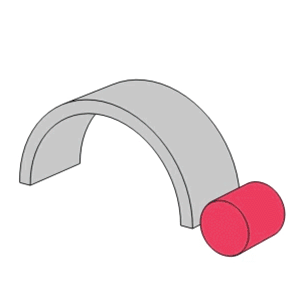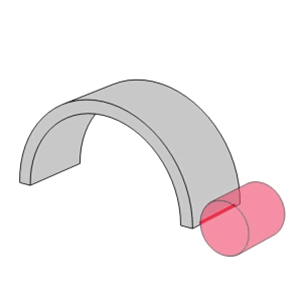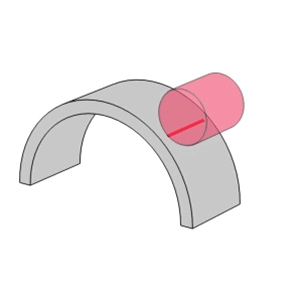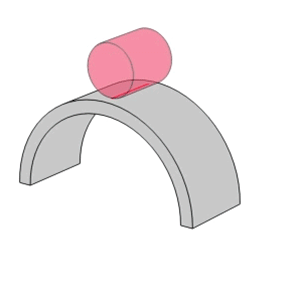
Line contact
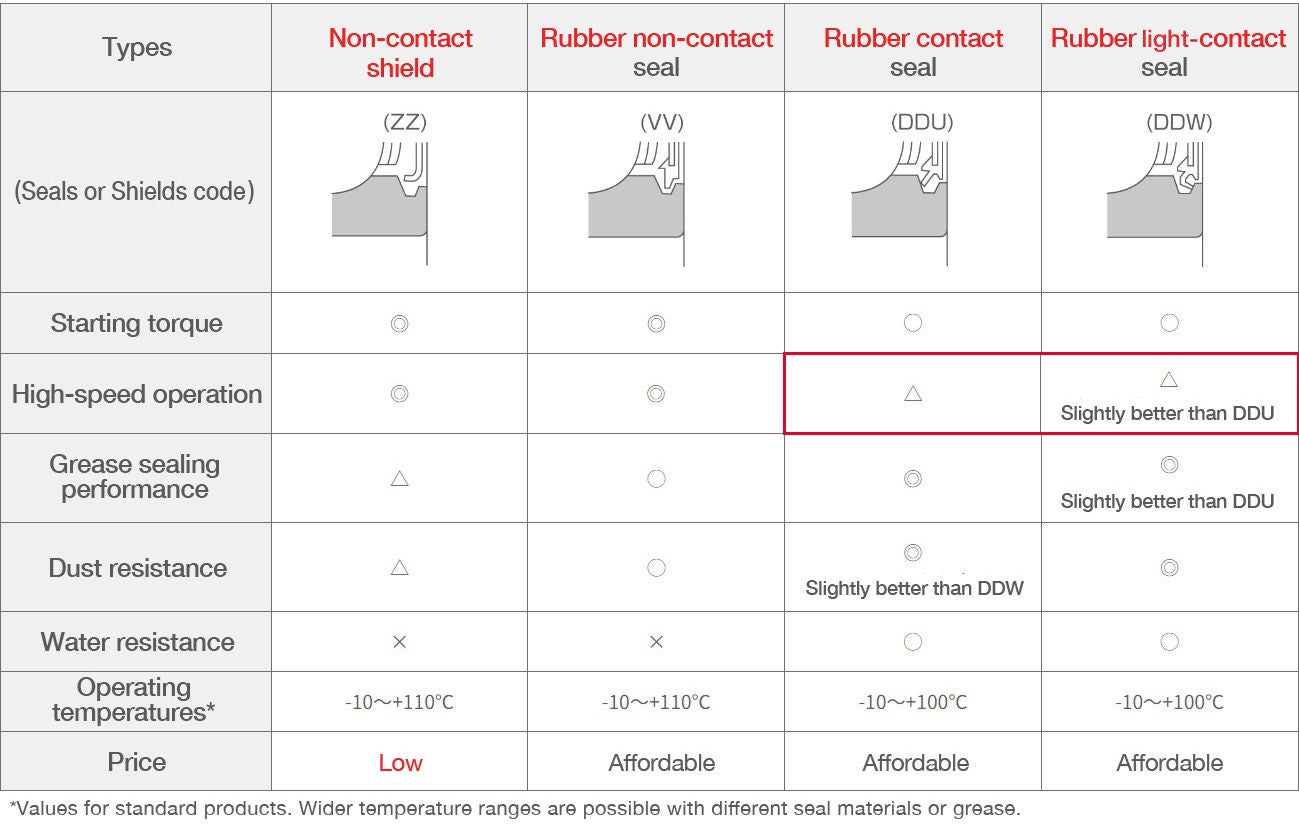
Seals/Shields for Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Seals and shields help to prevent foreign matter from entering the bearing and lubricant from leaking out. Bearings that utilize seals or shields are called “sealed bearings”.
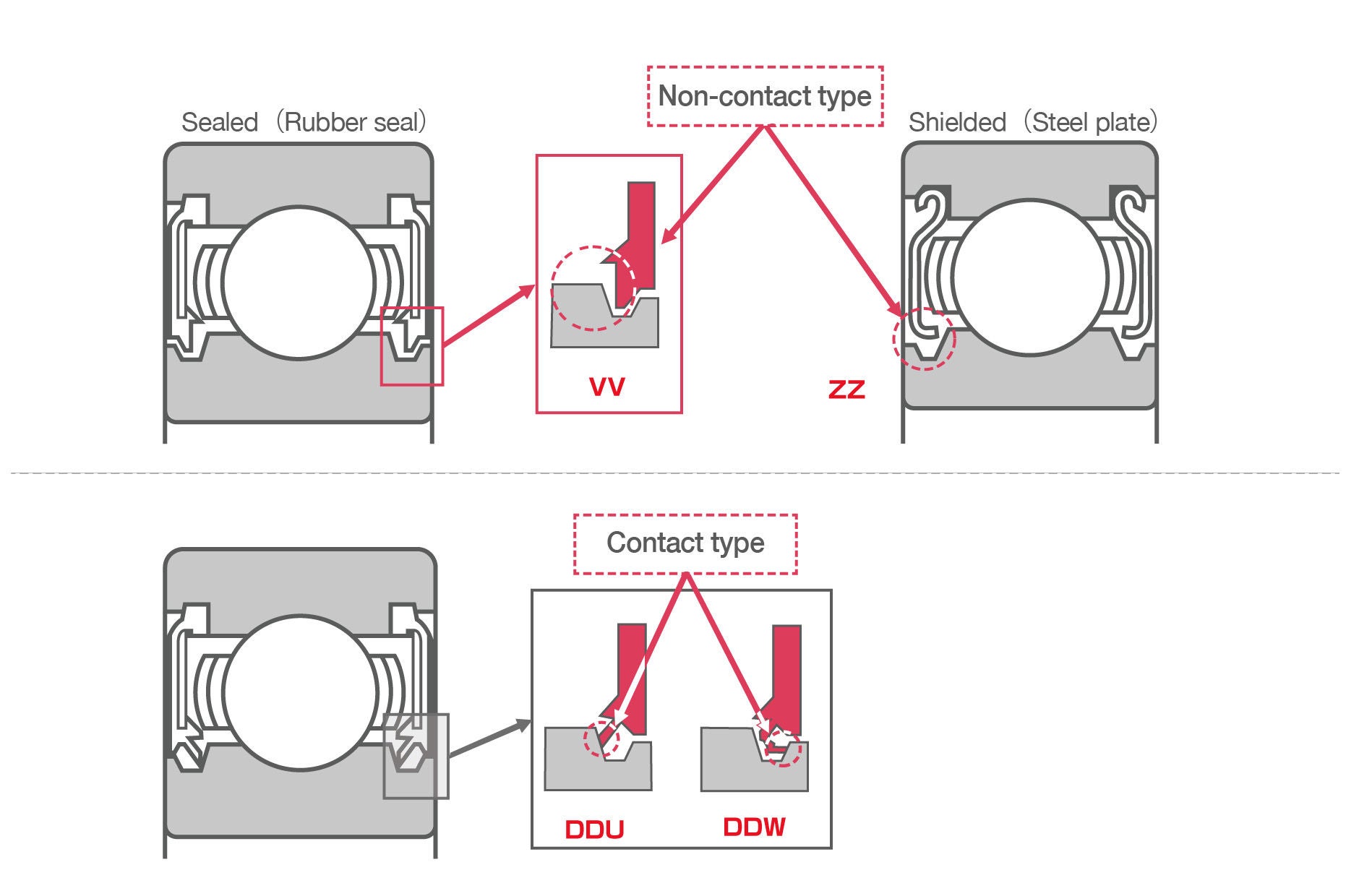
Features of Sealed Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Sealed ball bearings and sealed roller bearings are classified by the material and configuration of their seals/shields.
Table Key: ◎: Excellent ◯: Good △: Acceptable ×: Unsuitable