5—Bearing Designations
Bearing designations (bearing numbers) are codes that provide information about the design of a bearing. The basic designation uses definitions specified by ISO/JIS, while the meanings of codes in the supplementary (auxiliary) designation may be unique to the bearing manufacturer.
Formulation of Designations
The designation of a rolling bearing indicates its type, boundary dimensions, dimensional and running accuracies, internal clearance, and other specifications. It consists of two parts:
Basic Designation:
A code indicating the bearing type and important dimensions.
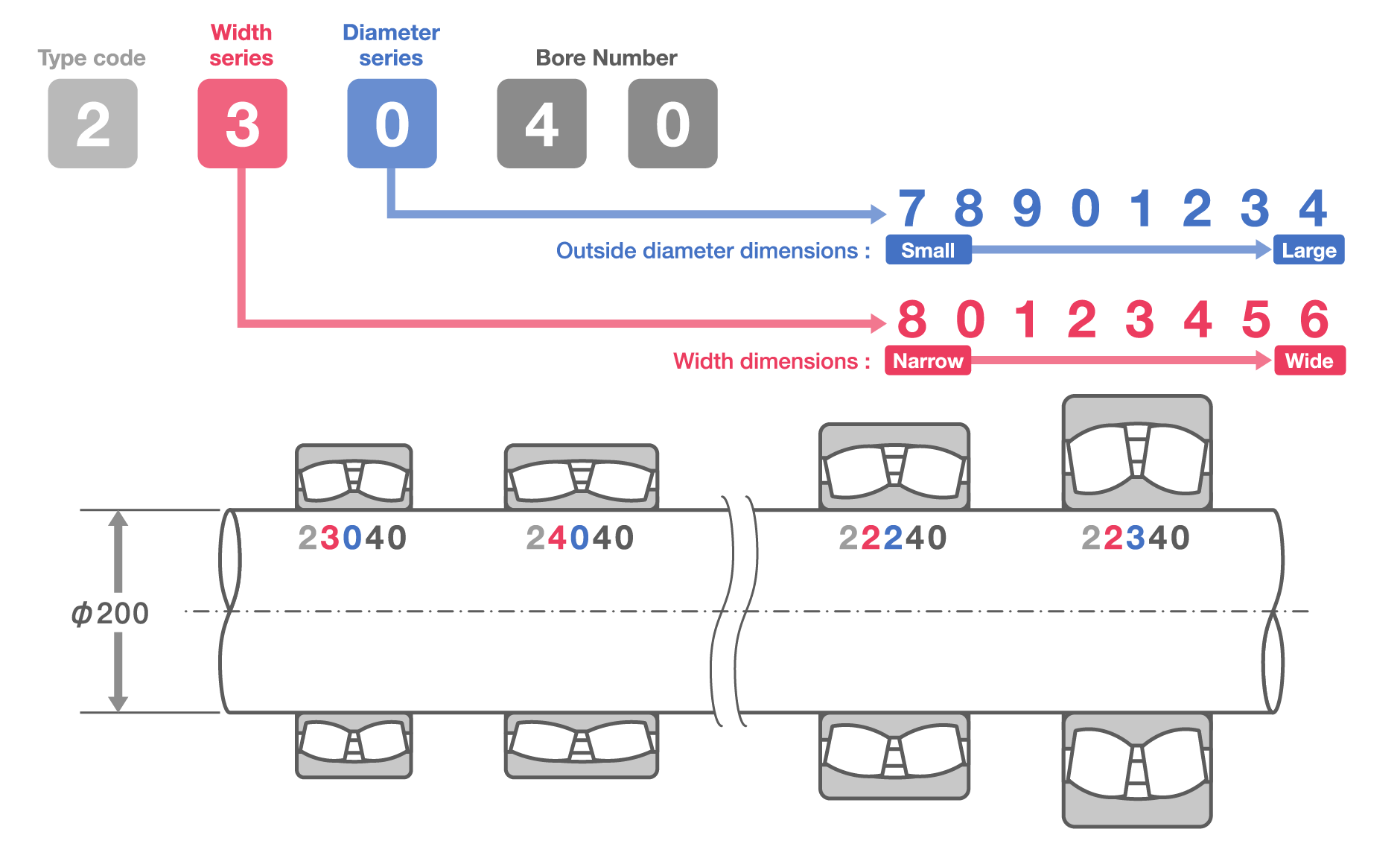
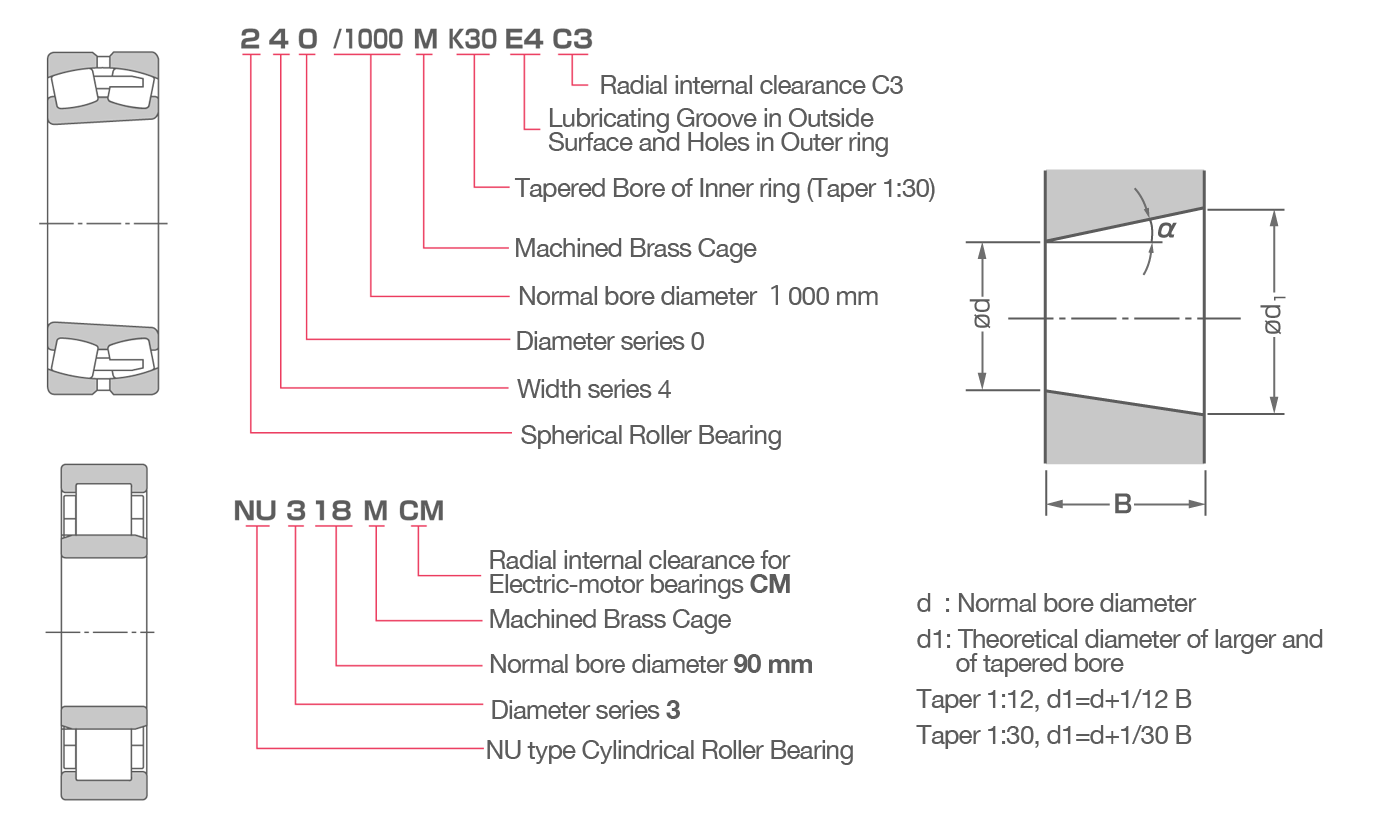
The first part is called the bearing series. After the type code, dimensions are specified with one or two digits indicating width/height and diameter, though the width code is sometimes omitted. The series is followed by codes for bore number and contact angle.
Supplementary Designation:
A code indicating bearing specfications, including design, material, cage type, and so on.
Though usually indicated in full on packaging, bearing designations may be abbreviated or omitted on certain components or documentation.
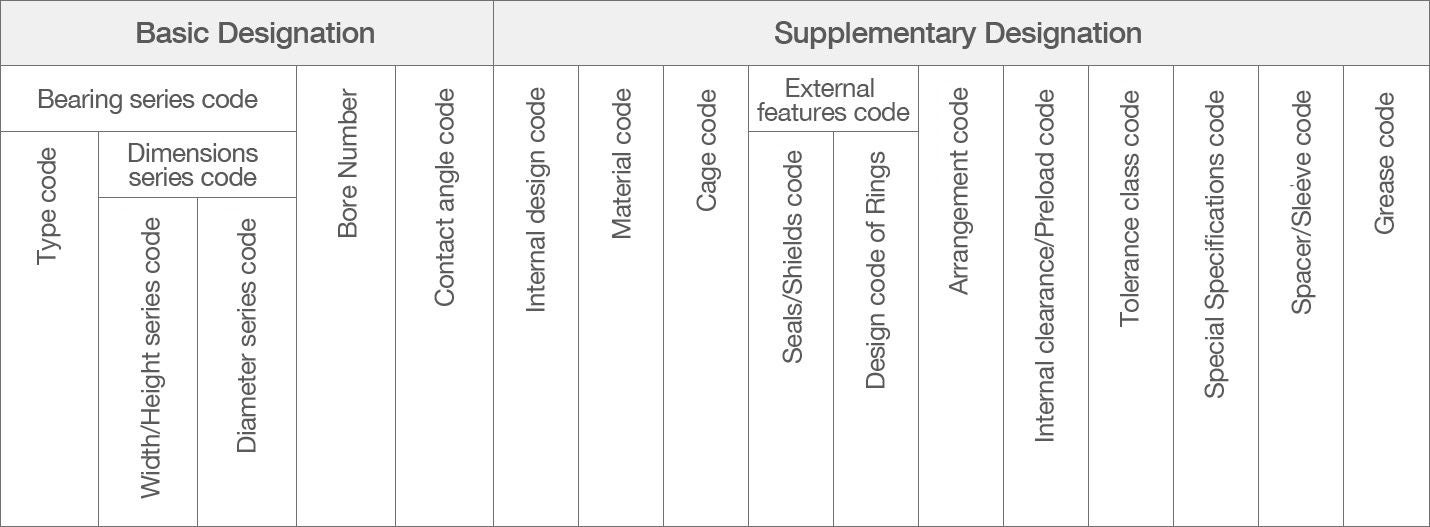
Radial Bearings: Basic Designations
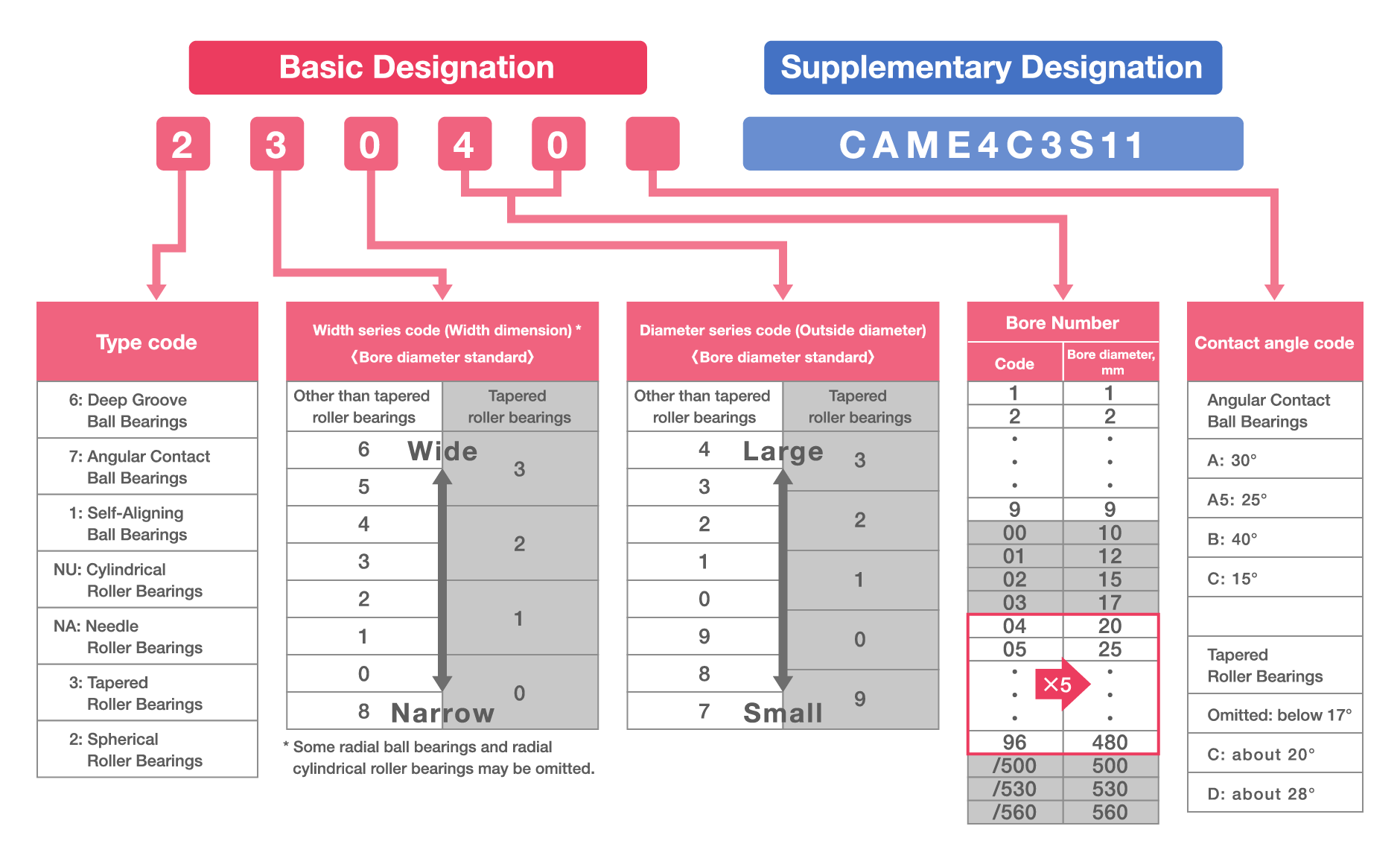
Radial Bearings: Width and Diameter Series
Bearing Series Designations
| Bearing Type | Series | Type | Dimensions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Width | Diameter | |||
| Single-row deep groove ball bearings | 68 69 60 62 63 | 6 6 6 6 6 | (1) (1) (1) (0) (0) | 8 9 0 2 3 |
| Single-row angular contact ball bearings | 79 70 72 73 | 7 7 7 7 | (1) (1) (0) (0) | 9 0 2 3 |
| Self-aligning ball bearings | 12 13 22 23 | 1 1 (1) (1) | (0) (0) 2 2 | (0) (0) 2 2 |
| Single-row cylindrical roller bearings | NU10 NU2 NU22 NU3 NU23 NU4 | NU NU NU NU NU NU | 1 (0) 2 (0) 2 (0) | 0 2 2 3 3 4 |
| NJ2 NJ22 NJ3 NJ23 NJ4 | NJ NJ NJ NJ NJ | (0) 2 (0) 2 (0) | 2 2 3 3 4 | |
| NUP2 NUP22 NUP3 NUP23 NUP4 | NUP NUP NUP NUP NUP | (0) 2 (0) 2 (0) | 2 2 3 3 4 | |
| N10 N2 N3 N4 | N N N N | 1 (0) (0) (0) | 0 2 3 4 | |
| NF2 NF3 NF4 | NF NF NF | (0) (0) (0) | 2 3 4 | |
| Bearing Type | Bearing Series | Type | Dimensions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Width/Height | Diameter | |||
| Double-row cylindrical roller bearings | NNU49 NN30 | NNU NN | 4 3 | 9 0 |
| Needle roller bearings | NA48 NA49 NA59 NA69 | NA NA NA NA | 4 4 5 6 | 8 9 9 9 |
| Tapered roller bearing | 329 320 330 331 302 322 332 303 323 | 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 | 2 2 3 3 0 2 3 0 2 | 9 0 0 1 2 2 2 3 3 |
| Spherical roller bearings | 230 231 222 232 213(1) 223 | 2 2 2 2 2 2 | 3 3 2 3 0 2 | 0 1 2 2 3 3 |
| Thrust ball bearings with flat back face | 511 512 513 514 522 523 524 | 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 | 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 | 1 2 3 4 2 3 4 |
| Spherical roller thrust bearings | 292 293 294 | 2 2 2 | 9 9 9 | 2 3 4 |
Note (1) Bearing Series 213 would logically be 203, but customarily it is numbered 213.
Remarks Numbers in parentheses in the width column are usually omitted from the designation.
Ball Bearing Designations
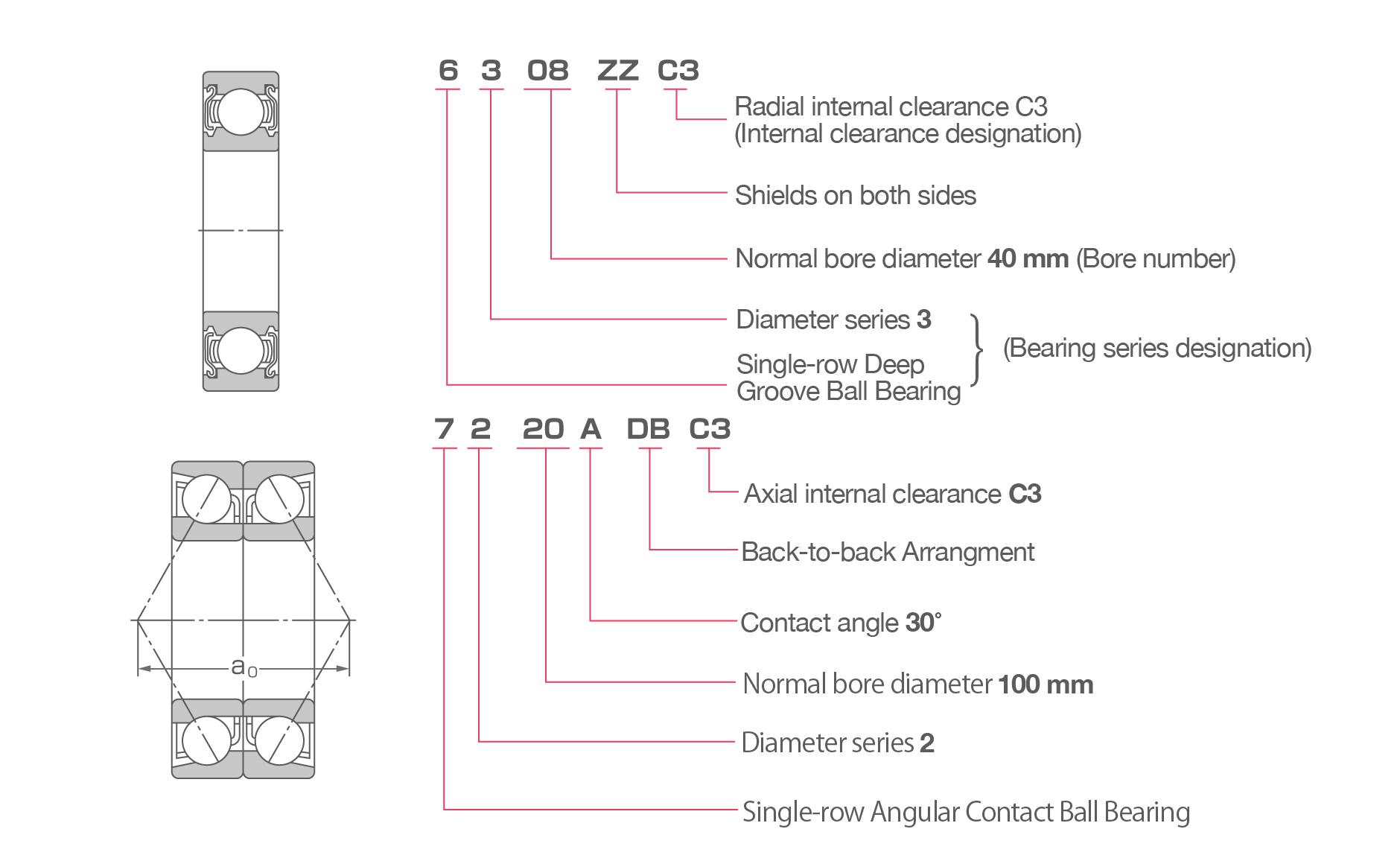
Roller Bearing Designations
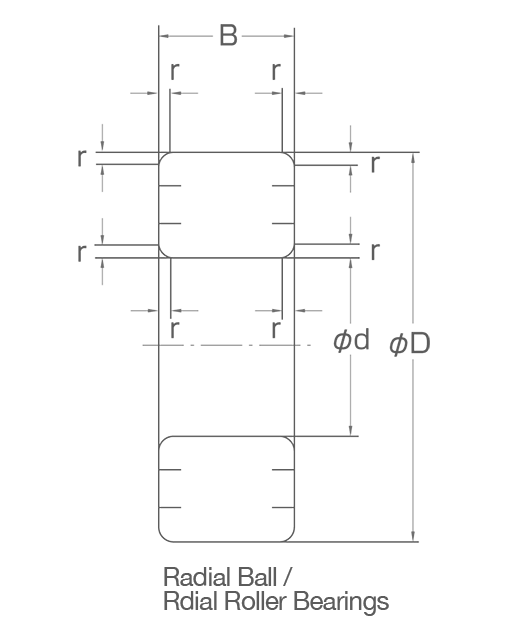
Radial Bearings: Boundary Dimensions
Radial ball/roller bearing
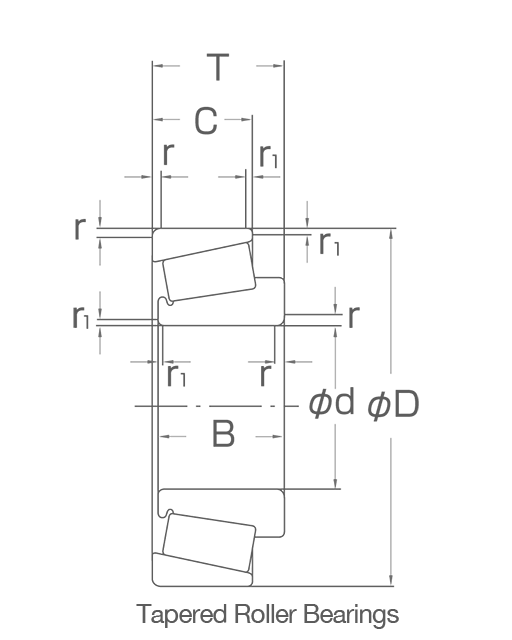
Tapered roller bearing
What are boundary dimensions?
Boundary dimensions define the important external geometry of a bearing. They are:
- Bearing bore d,
- Bearing outer diameter D,
- Bearing width (or inner ring width) B,
- Outer ring width C,
- Assembled width T, and
- Main chamfer dimensions r, r1
These dimensions are crucial in mounting the bearing to the shaft or housing.
Boundary dimensions are specified by ISO, allowing standard products to be interchangeable.
