2.2—Angular Contact Ball Bearings
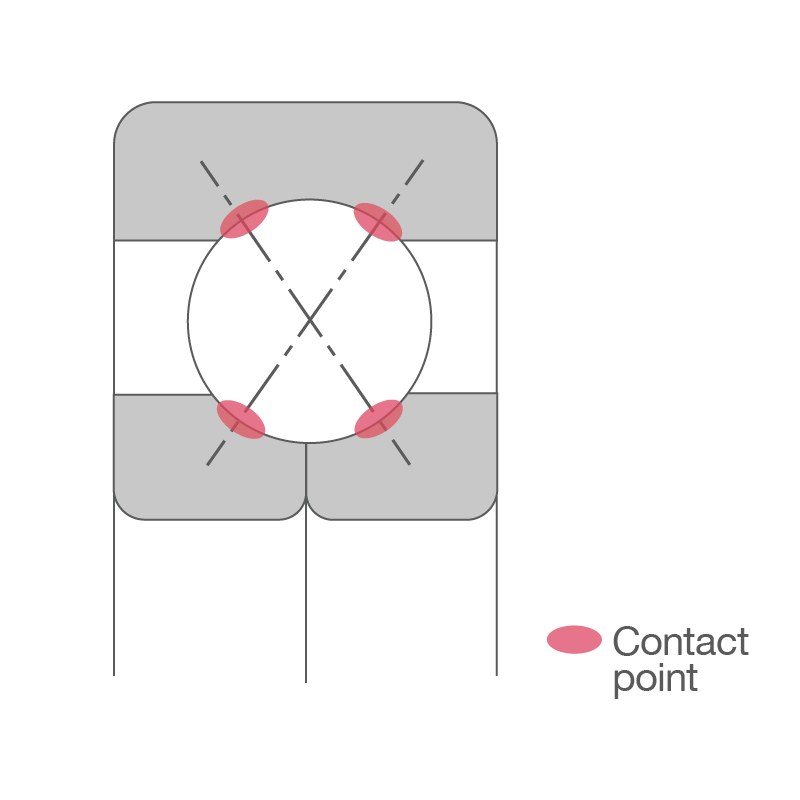
Angular contact ball bearings can support radial loads and axial loads in one direction.
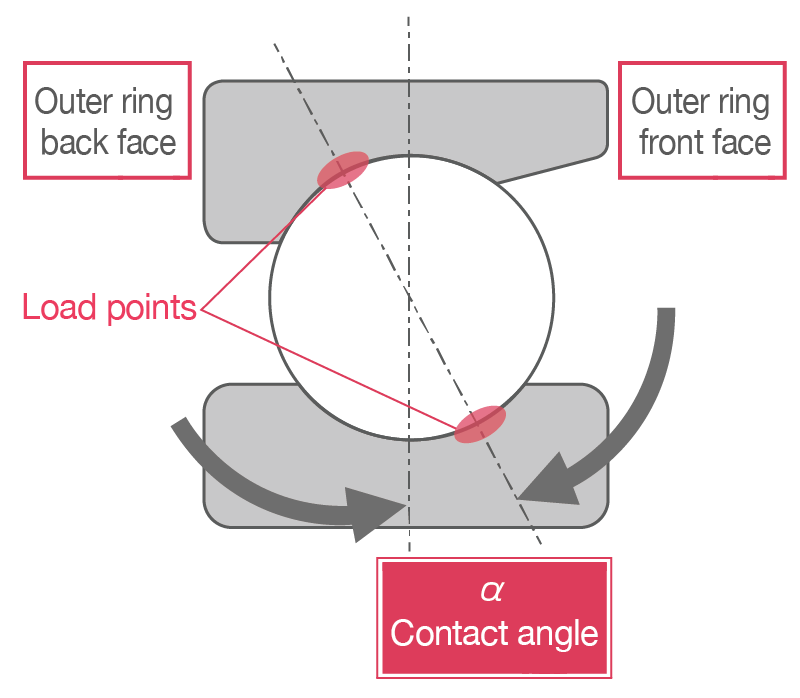
The line along the points where the balls contact the rings is inclined relative to the radial direction of the bearing. Due to this contact angle (α), an axial force is generated when a radial load is applied. Typically, double-row bearings or multiple bearing sets called arrangements are mounted to bear the axial component.
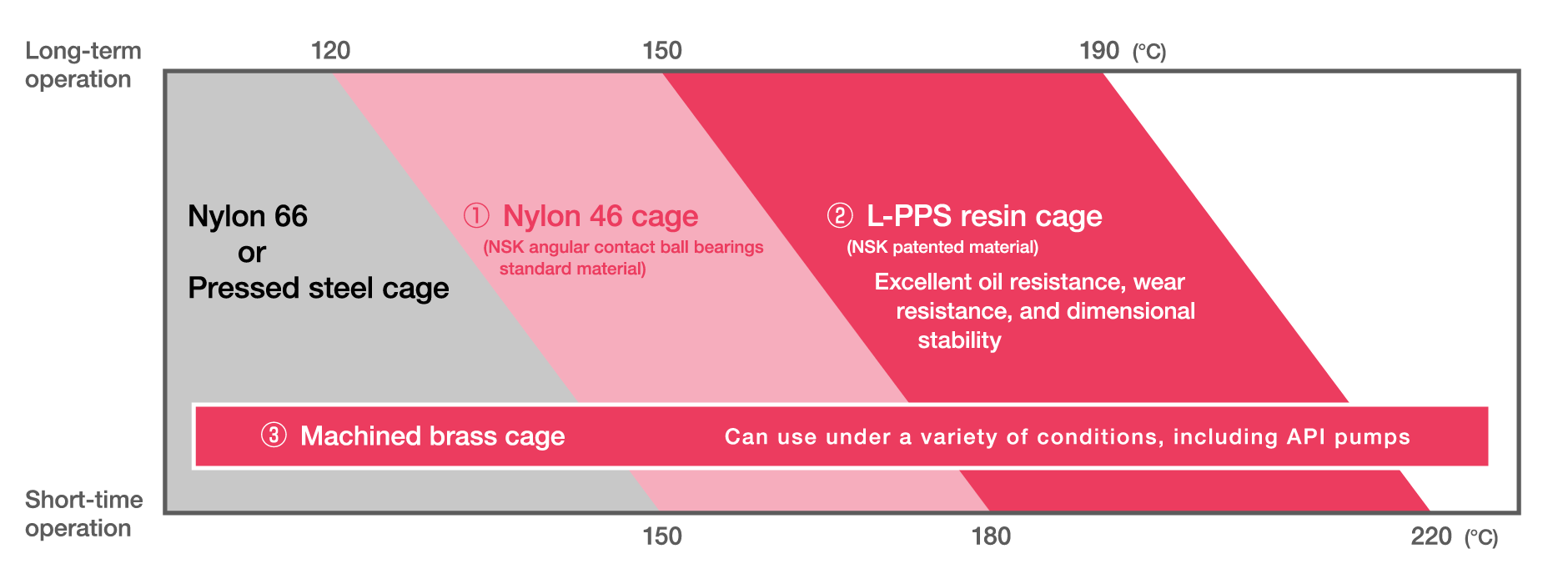
Generally, cages are made of pressed steel, but polyamide resin cages are sometimes used in high-precision bearings with contact angles of 30° or less.
Changing the arrangement configuration can provide different load-carrying characteristics.
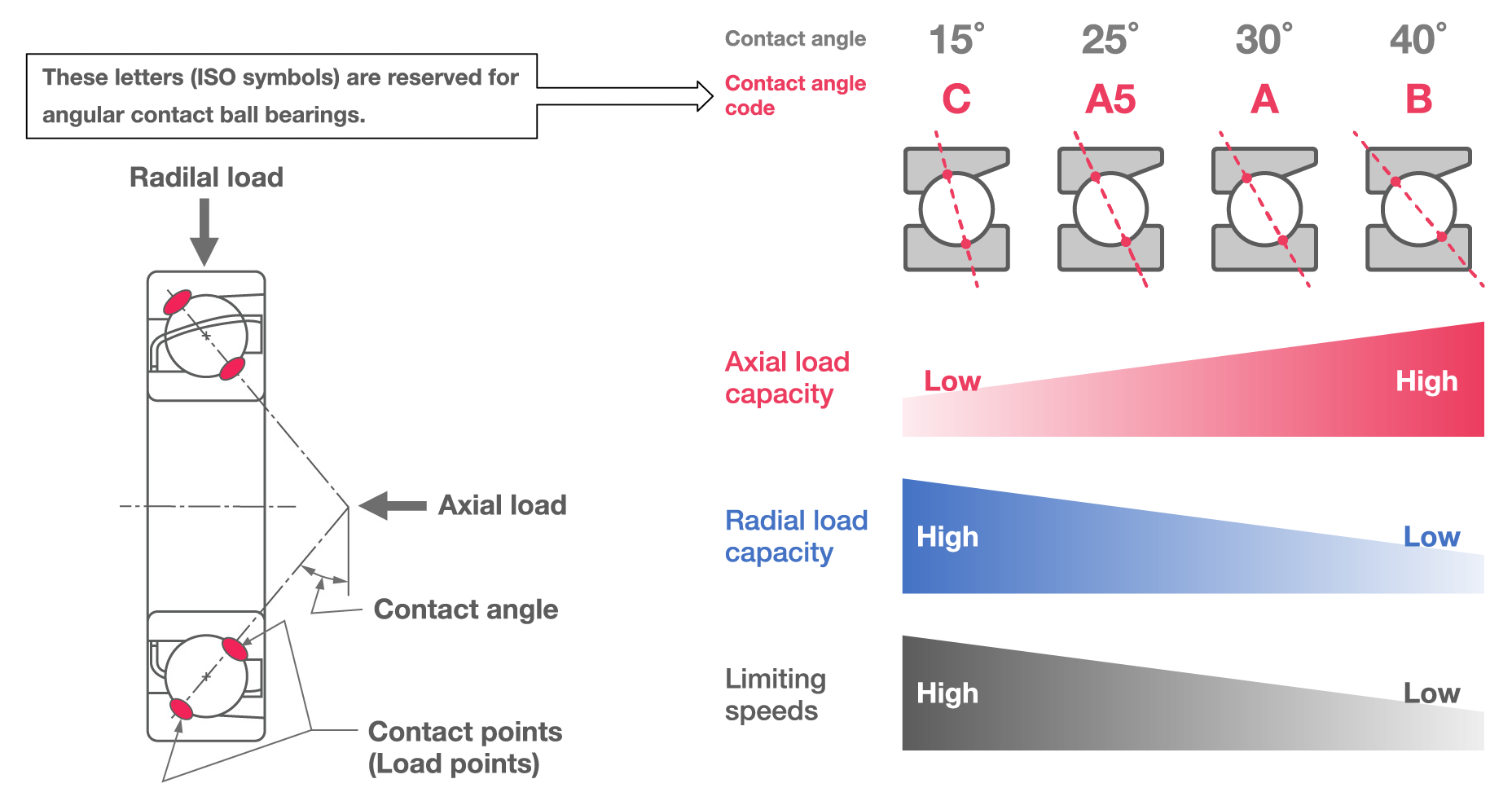
Contact Angles
The contact angle of angular contact ball bearings allows them to sustain significant unidirectional axial loads and some radial load. The contact angle is indicated in the bearing designation with standardized codes.

Cages for Angular Contact Ball Bearings

Pressed steel cage

Polyamide resin (Nylon-46) cage

Machined-brass cage
A heat treatment for dimensional stability can be applied to the rings and balls to allow the bearing to operate long-term at 120°C or higher.
Bearing Arrangements: Types and Characteristics
Bearing arrangements consist of two or more ball or roller bearings combined into a set with two or more rows.
Some features of two-bearing arrangements (paired mountings) of angular contact ball bearings are shown below.
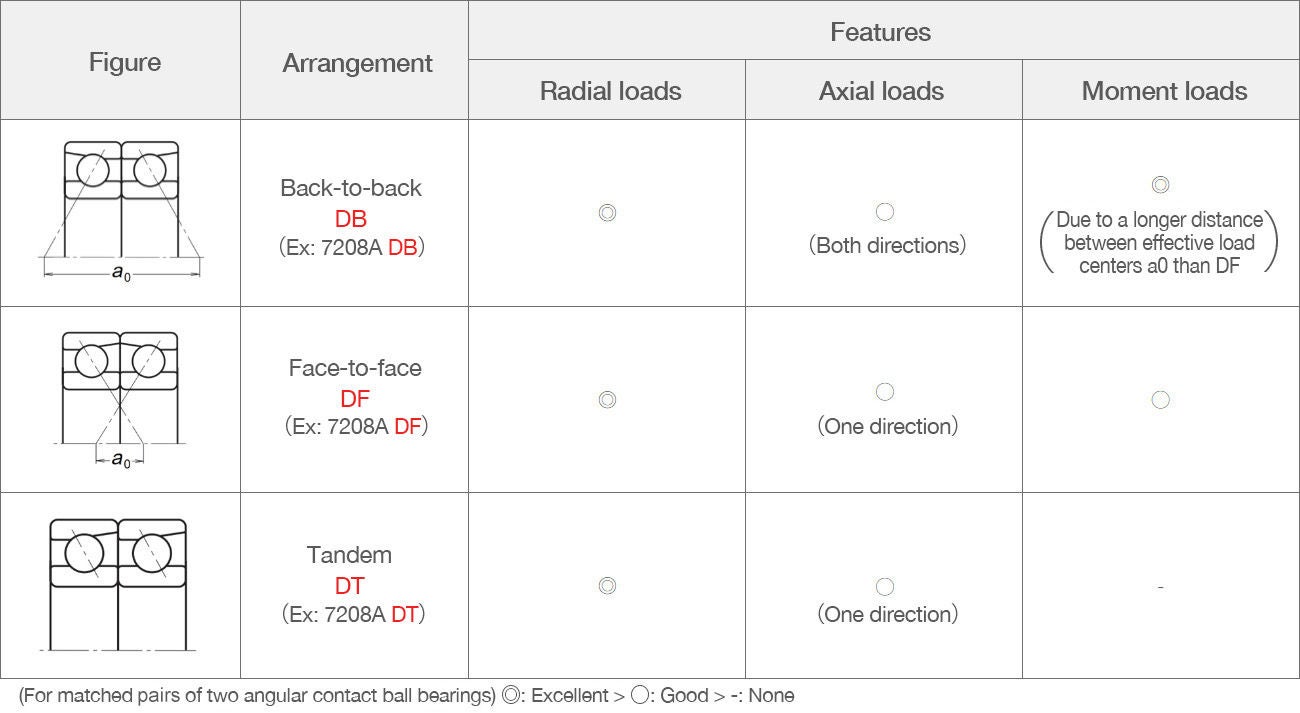
Arrangement Codes
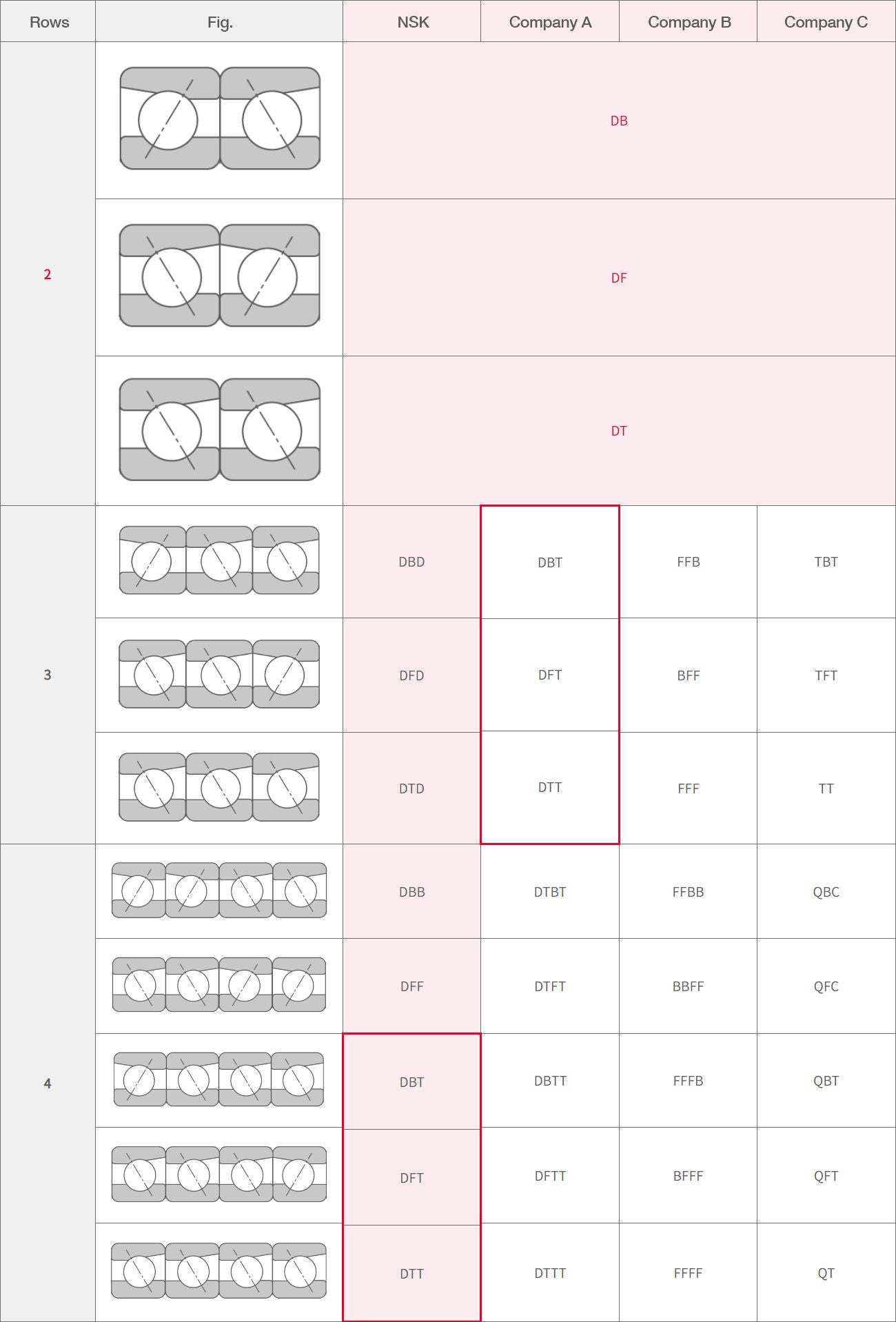
Note: Identical arrangement codes from different companies can have different meanings.
Double-Row Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Double-row angular contact ball bearings are essentially a back-to-back (DB) arrangement of two single-row angular contact ball bearings that share a single inner and outer ring.
These bearings can support radial loads, axial loads in both directions, and moment loads.
- They are smaller in width than an arrangement of two bearings with the same outside diameter/bore dimensions.
- Four types of single-row angular contact ball bearings are available with different contact angles (15°, 25°, 30°, and 40°), while double-row angular contact ball bearings (5xxx) have a contact angle of 25°.
- Cages are typically made of pressed steel.
- These bearings are commonly used in pumps, electric motors, and blowers.
Comparison of 5206 (double-row) and 7206ADB (arrangement)
| 5206 | 7206ADB(M) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bore Diameter (mm) | 30 | ← | |
| Outer Diameter (mm) | 62 | ← | |
| Width (mm) | 23.8 | 32 | |
| Contact Angle (°) | 25 | 30 | |
| Basic Load Ratings (kN) | Dynamic | 29.6 | 36.5 |
| Static | 21.1 | 29.5 | |
| Limiting Speeds (min-1) | Grease | 7,100 | 10,000 |
| Oil | 9,500 | 13,000 | |
Comparison of Double-Row Angular Bearings (3xxx to 5xxx)
| Designation | 3xxx (compared to 5xxx) | |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensions | Identical | |
| Dynamic Load Rating | Low*1 | |
| Internal Design*1 | Outer Ring | Fill slot present(absent in 5xxx)*2 |
| Inner Ring | 1 row(5xxx:2 row raceway groove) | |
| Balls | Numerous | |
| Ball Diameter | Small | |
| Contact Angle | Large | |
Notes
*1 Some products from other companies have the same internal design for both 3xxx and 5xxx series bearings.
*2 Some products from other companies do not have visible fill slots and use split inner ring.
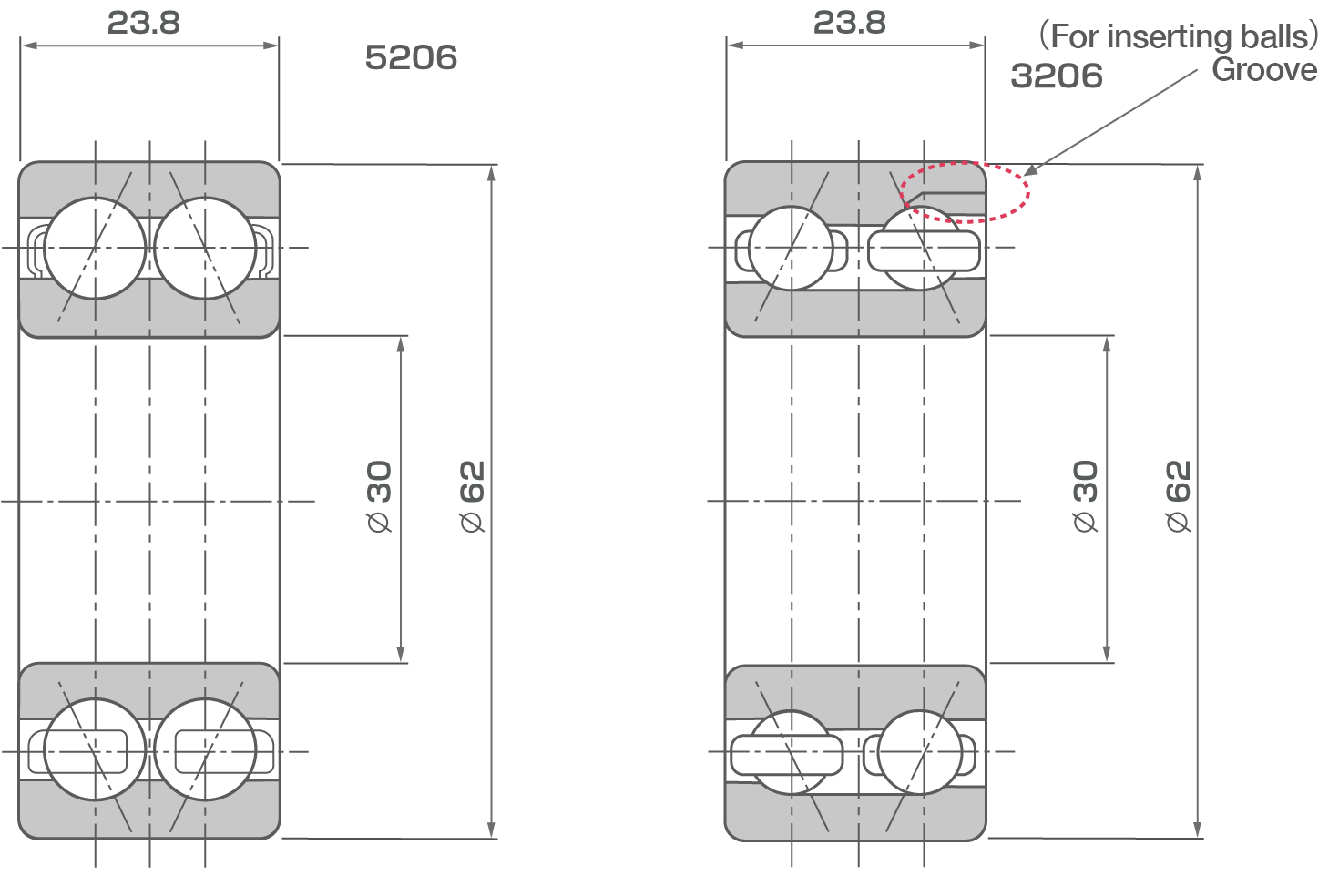
*In 3xxx, take care to ensure that the area where load is applied to the bearing (loaded zone) does not include the filling slot.
Four-Point Contact Ball Bearings
- Four-point-contact ball bearings are single-row angular contact ball bearings with a separable inner ring.
- These bearings can support radial loads and axial loads in both directions.
- With a contact angle of 35°, they are well-suited for pure axial loads or combined loads where the axial portion is high.
- A single four-point-contact bearing can replace a DF (front-to-front) or DB (back-to-back) arrangement.
- Cages are typically made of machined brass.