NSK Ltd.
Corporate Communications Department
NSK Develops Practical Magnetostrictive Torque Sensor for Automobiles
Smaller and lower cost compared to conventional model,
and planned for application widely in various types of mobility
●Newly developed torque sensor has smaller structure and lower cost compared to conventional model, simultaneously delivers reliability, compactness, and cost-competitiveness
●New sensor is widely applicable not only to automotive powertrains but also actuators, e-bike drive units, and various other types of mobility
NSK Ltd. has developed a practical magnetostrictive torque sensor (3rd-generation sensor) for automobiles which enables failure prediction, a comfortable ride, extension of driving mileage and performance improvement thanks to its weight-reducing and space-saving features, while also shortening the development period.
The newly developed product is scheduled to be exhibited at the Automotive Engineering Exposition 2024 Yokohama to be held at Pacifico Yokohama on May 22-24, 2024. NSK also plans to make a joint presentation about the product at the 2024 JSAE Annual Congress (Spring) to be held at the same venue.
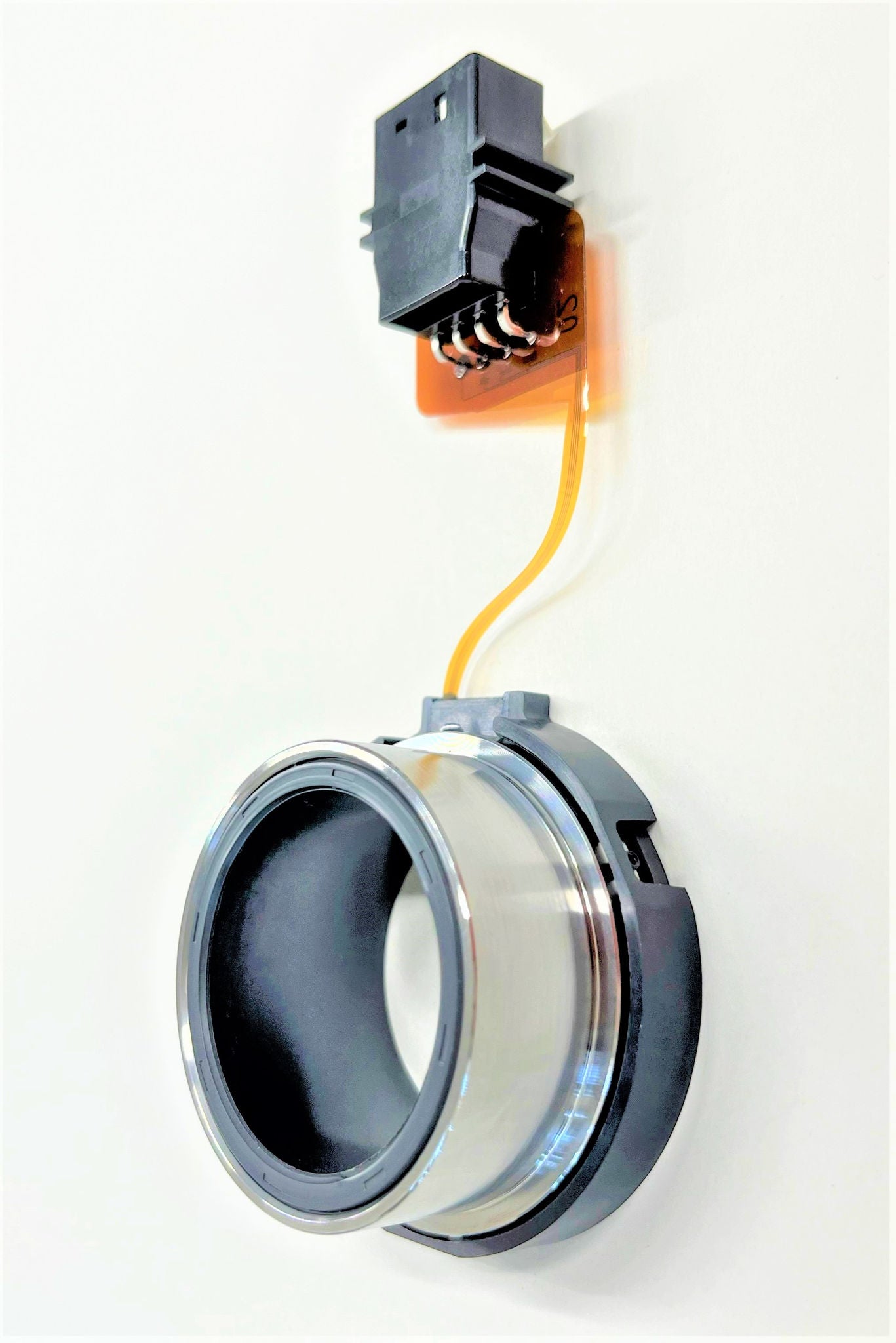

Newly developed product (third-generation sensor)
1.Background
1) Needs for magnetostrictive torque sensors for automobiles
Magnetostrictive torque sensors are a contactless-type sensor used to measure the torque by detecting shaft torsion magnetically. The automobile manufacturer can utilize the torque sensor in vehicles for system control using the torque information detected. For example, NSK has successfully demonstrated the extension of driving mileage by controlling gear-shifting or hydraulic pressure with the torque sensor equipped in the automotive powertrain. (See torque sensor installation example below.) So, many customers expect to use NSK’s torque sensor not only to extend driving mileage but also to offer failure prediction, a comfortable ride, and performance improvement thanks to its weight-reducing and space-saving features, as well as its potential to shorten the period of vehicle development. These benefits are driving an increasing demand for automotive torque sensors, accompanying today’s electrification and automation trends.
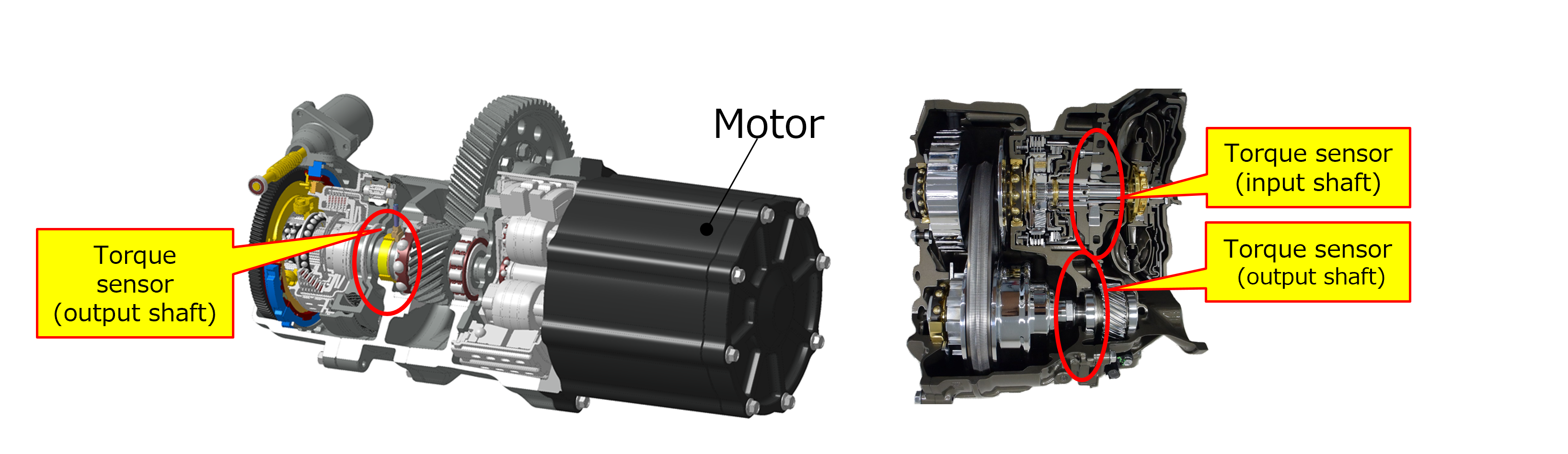
Torque sensor installation example (Left: 2-speed transmission output shaft; Right: Belt-type CVT input and output shafts)
2) Development challenges
Magnetostrictive torque sensors have become commonplace in the drive unit of e-bikes, but they have not been put into practical use in automobiles due to the difficulty of adapting them to survive more severe operating environments.
In order to realize a torque sensor for automotive applications, both the torque sensor and the drive shaft whose torque is detected are required to satisfy the three requirements of reliability, compactness, and low cost simultaneously. For example, since the torque sensor will be installed in a harsh environment involving oil, steel dust, large temperature fluctuations and vibrations, it needs to be robust and reliable to ensure stable measurements. But on the other hand, the sensor must be small and inexpensive, with a simple structure.
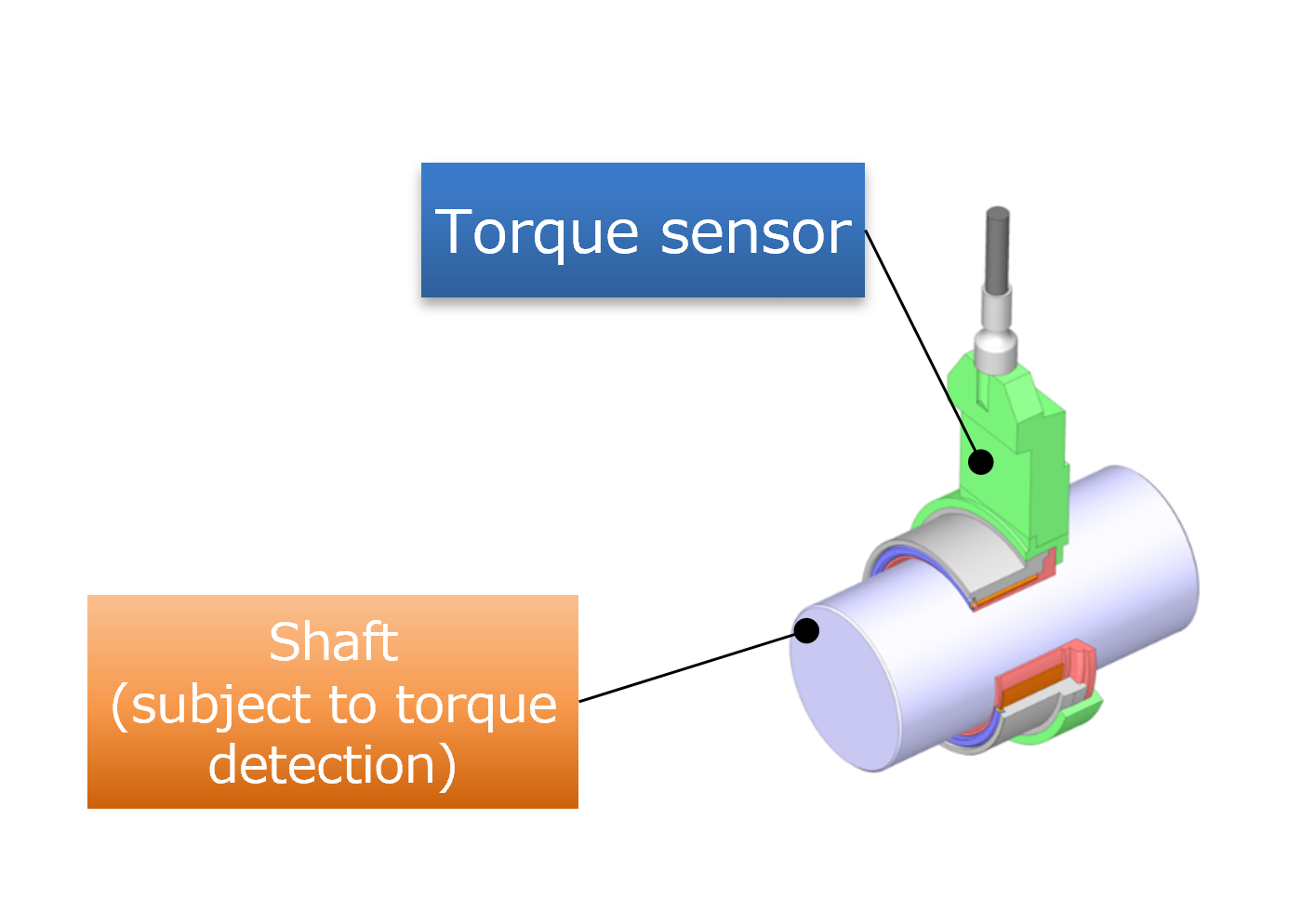
Vehicle driveshaft and torque sensor for detecting its torque
3) Development history
In July 2020 NSK developed a non-contact torque sensor for automobiles (first-generation sensor), and then successfully achieved torque detection applicable to the general specifications of automotive driveshafts. However, although the torque sensor featured a simple, slim structure, it needed to be improved in terms of the reliability of actual applications. Accordingly, NSK made continuous improvements in a process of technical communication with customers, receiving their feedback on validation tests in application, and in 2022 developed a second-generation sensor with increased reliability. The new product announced today is the third-generation torque sensor, developed as practical model for automotive applications.
2. Overview of the newly developed torque sensor
Smaller and lower cost compared to second-generation sensor.
1) Downsizing:
Approximately 45% reduction of sensor volume has been achieved thanks to the elimination of the conversion section from FPC to cable via terminals by utilizing the FPC* not only as a sensor coil but also as a cable
2) Cost reduction:
Approximately 40% reduction of parts number has been achieved thanks to the integration of the outer cover and the bobbin in addition to the elimination of the conversion section from FPC to cable. A simplified assembly method with pins and material change of the back yoke to bearing steel, in consideration of procurement, has also been implemented.
*FPC: Flexible printed circuit. A bendable printed circuit board made from a thin insulator (polyimide film) and copper foil.
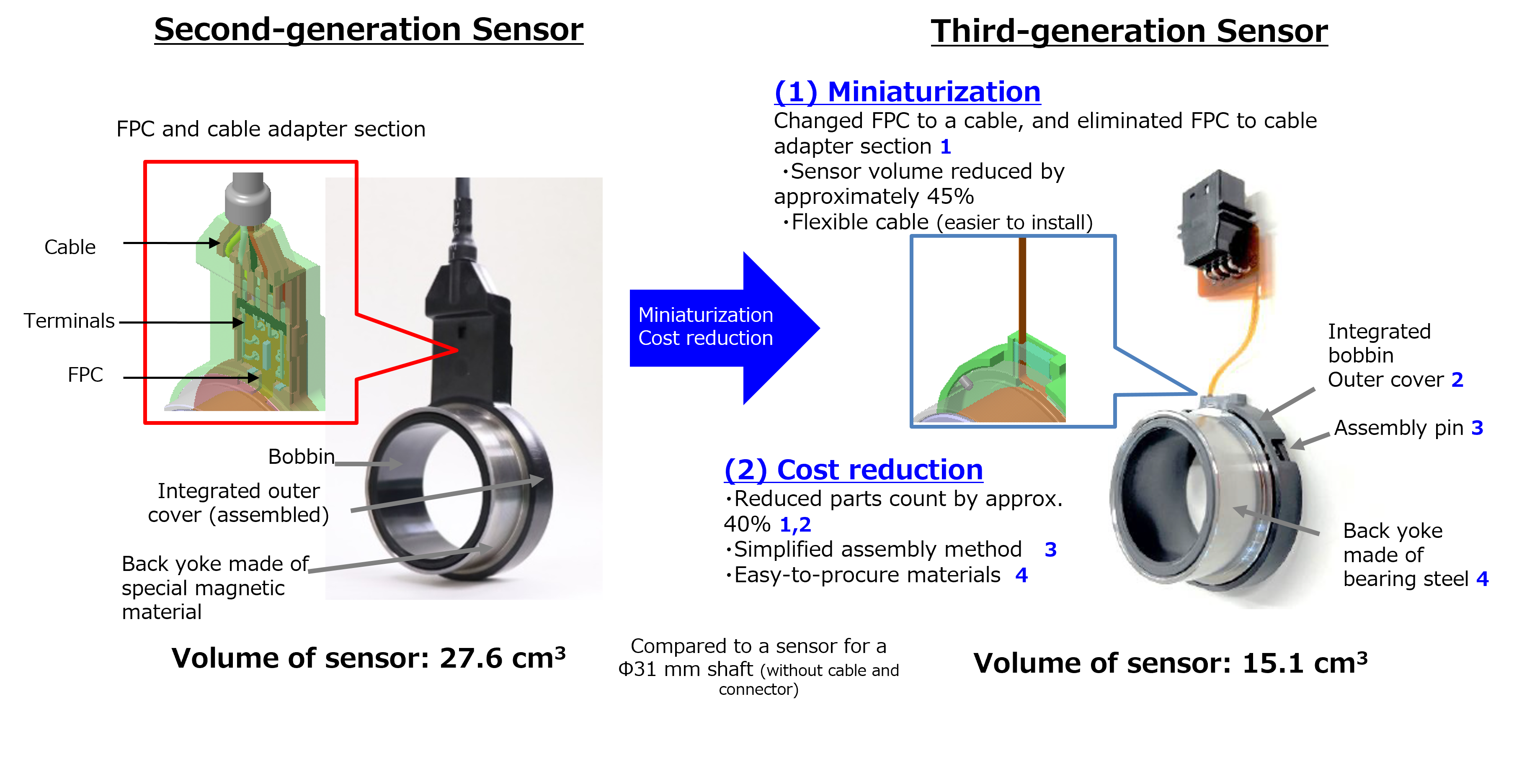
Second-generation (left) and third-generation (right)
3. Summary
1) The sensor achieves applicability to automobiles by simultaneously implementing reliability, compactness, and low cost, leveraging NSK’s years of know-how.
2) The sensor is applicable not only to automotive powertrains but also actuators, e-bike drive units, and various other types of mobility thanks to its compactness.
3) The sensor enables failure prediction, a comfortable ride, extended driving mileage and performance improvement thanks to its weight-reducing and space-saving features, while also shortening the development period.
About NSK
NSK began its journey manufacturing the first bearings in Japan in 1916, and has since developed into a global organization researching, designing, and manufacturing Motion & Control™ solutions essential for mobility and industrial applications. NSK is the top supplier of bearings in Japan and is the third largest supplier in the world by market share.
Our responsive products and technologies enhance automotive performance and industrial productivity while reducing energy consumption to unprecedented low levels. In the early 1960s, we set our sights outside Japan and have established over 200 business locations in 31 countries alongside a vast network of joint ventures and partnerships in all corners of the world.
