Introduction to Bearings
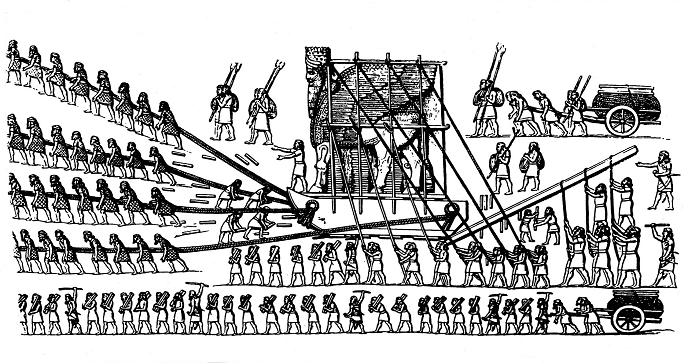
Bearings work under the principles of rolling and sliding motion, concepts known to humans throughout history, with this example of construction in ancient Mesopotamia dating back to around 800 B.C.
Much later, the famous genius of the Renaissance Leonardo da Vinci came up with an idea for a structure that is remarkably like that used in modern rolling bearings. The machine-based civilization born in the Industrial Revolution of the 18th century led to the rapid development of modern bearings.
In 1916, NSK started the first specialist production of bearings in Japan; however, it was not until after the end of the Second World War that Japan's bearing technology made substantial progress. 1955 marked the beginning of growth in demand for private automobiles, in addition to home appliances such as washing machines, refrigerators, and air conditioners.
In this environment, Japanese consumers insisted that appliances be quiet. However, bearing manufacturers outside Japan placed little emphasis on controlling noise, so Japanese manufacturers proceeded to build up knowhow through research and development efforts aimed at developing the world’s quietest bearings. Later, Japanese bearings renowned for their quietness were exported to the United States and Europe, with continued development bringing great advancements in durability and reliability. More recently, bearing specifications have become standardized in accordance with international ISO standards.
Today, Japanese-made bearings are admired around the world for their high performance and high quality. There are said to be around 3 billion bearings made annually in Japan, of which over 40% are for automobile use. Nearly 30% are exported.
Bearings continue to be developed and improved globally, with research focused on further reducing friction in response to changing needs. NSK and other bearing makers continue intensive R&D efforts aimed at:
- reducing weight
- making bearings more compact
- extending life
- saving energy, and
- reducing environmental impacts
Anything that can be called a machine invariably incorporates bearings in some capacity. Bearings must fulfill a great variety of needs, and they are constantly evolving to meet changing requirements and new applications.
Speed & Precision: 400,000 RPM Micro-Bearings
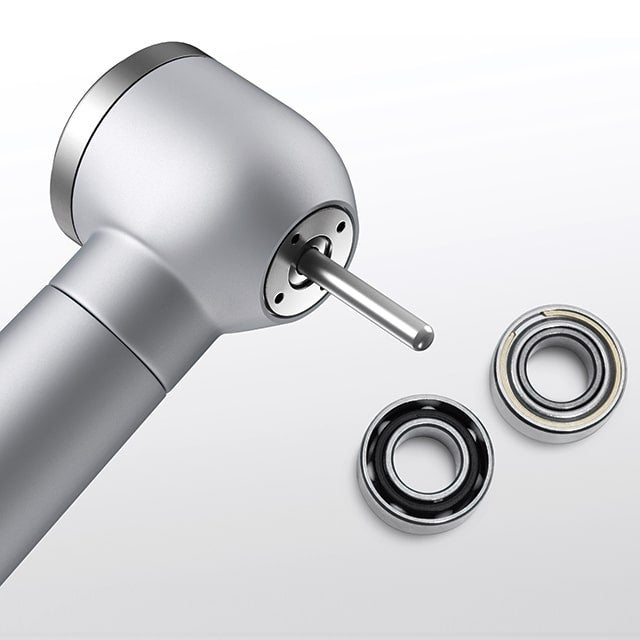

Dental drills use specialized bearings that can rotate at ultra-high speeds. This air turbine handpiece uses ultra-high precision bearings with an inner diameter of 3 mm, an outer diameter of 6 mm and a width just over 2 mm, though even smaller bearings exist.
These bearings support astounding speeds of 400,000 rotations per minute. This ultra-high speed, together with extremely accurate rotation, almost eliminates vibration in the handpiece, helping ensure safe and comfortable treatment.
From Micro to Massive—Bearings Come in All Sizes
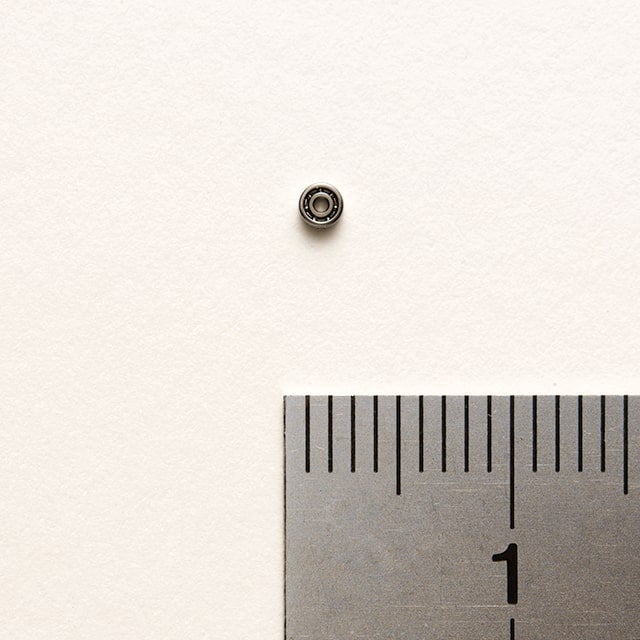

The dimensions of bearings vary widely: The world’s smallest miniature bearings have an inner diameter of 0.6 mm, an outer diameter of 2 mm, and a width of 0.8 mm for use in ultra-compact motors.
At the other extreme, there are giant bearings with an outer diameter of 6 meters that weigh over 15 tons. These huge components are used in giant boring machines for digging tunnels like the Channel Tunnel linking France and Britain under the Strait of Dover.
Bearings Keep Us Soaring Safely
Bearings are also used in the main shafts of V2500 jet engines in international passenger airplanes. The rolling elements in these bearings move at a speed of 160 meters per second, equivalent to 580 km/h. The next time you fly, you can sit back and marvel at how high-performance, high-speed bearings maintain the fast, powerful, and extended operation of jet engines.
Nanometer Level Accuracy
It’s not an exaggeration to say that the accuracy of a machine is determined by the rotational accuracy of the bearings within. A bearing supports each end of an axis of rotation. If there is excessive runout from the center of that axis, a machine cannot be expected to operate with high performance.
Ultra-high precision bearings can limit these errors to nanometer levels (for reference, 1 nm is equal to one billionth of a meter!) Deflection of the central axis in a PC hard disk drive is kept under 100 nm thanks to ultra-high precision bearings. This high level of precision is determined by strict controls for accuracy of the rolling elements during manufacturing.
Proven Performance Even in Space
Bearings are also essential to space development. Data in weather reports, TV broadcasts, and car navigation systems all come to us from satellites orbiting the earth. Each satellite has a piece of equipment known as a flywheel that maintains its correct position and orientation with the help of ultra-high precision bearings. Such bearings have been diligently rotating in space for over 15 years!
Standing Up to Extreme Temperatures
Smoothly rotating in liquid hydrogen at -253°C, bearings used in the liquid fuel pumps of space rockets face some of the coldest temperatures imaginable. At the other extreme, high-performance bearings in CT scanners and other medical equipment face intense heat. Even in a vacuum tube where X-rays are generated and temperatures reach 300 to 500°C, bearings continue to rotate, helping us to maintain our health.
With such a huge role to play in all machines that move, advancements in bearings wind up having huge effects on the world at large. Let’s look at some key areas where bearing engineers are directing their efforts.
Greater energy savings
The smaller a machine, the smaller its components. This downsizing comes with higher needs for precision, as even a small amount of friction can lead to a breakdown. Moreover, the total energy consumption of even the most compact equipment is massive when viewed on a global scale. To produce even greater energy savings, NSK continues to seek out even better ways of reducing friction with bearings.
Cleaner credentials
Refining bearing technology is a boon for the environment as improvements made to improve friction help reduce the energy used by equipment. In vehicles for example, compact bearings with lower friction can reduce vehicle weight and ensure smooth operation while improving fuel economy with fewer CO2 emissions. Additionally, most bearings are made from steel free of harmful chemical substances. Bearing steel can be recycled into new materials, and bearings themselves are excellent candidates for recycling and reuse.
Higher Comfort
In addition to fulfilling their function, machines must be both pleasant to use and safe for the environment. Though production has long been the focus, needs are shifting to prioritize equipment that helps individuals enjoy more fulfilling lives and that contributes to society through education, medical services, welfare, and entertainment. Work is underway to improve the adaptability of bearings for use in these new roles and functions.
NSK continues to hone R&D efforts on these themes for people and for the planet. Building on over 100 years of experience as a manufacturer of all types of bearings, NSK continues to strive to be at the forefront of new bearing technologies and applications now and long into the future.















